In this article you will find the translation of the main Photoshop tools and commands from English into Russian. The full version of the dictionary can be found at the link below.
File - File
New- Create (Ctrl+N)
open- Open (Ctrl+O)
Browse in Bridge- Browse in Bridge (Alt+Ctrl+O)
open as- Open as (Alt+Shft+Ctrl+O)
Open as Smart Object- Open as smart object
Open Recent- Latest Documents
close- Close (Ctrl+W)
Close All- Close all (Alt+Ctrl+W)
Close and Go To Bridge- Close and go to Bridge (Shift+Ctrl+W)
Revert- Restore (F12)
Export- Export >
Generate- Generate >
Place Embedded- Place embedded
Place Linked- Place related
package- To wrap up
Automates- Automation >
Scripts- Scenarios >
Import- Import >
file info- Information about the file (Alt+Shft+Ctrl+I)
print- Print (Ctrl+P)
Print One Copy- Print one copy (Alt+Shft+Ctrl+P)
exit- Exit (Ctrl+Q)
Edit - Editing
Undo- Undo (Ctrl+Z)
step forward- Step forward (Alt+Ctrl+Z)
Step backwards- Step back (Shift+Ctrl+Z)
Fade- Loosen (Alt+Ctrl+F)
Cut- Cut (Ctrl+X)
Copy- Copy (Ctrl+C)
Copy Merged- Copy merged data (Shift+Ctrl+C)
Past- Paste (Ctrl+V)
Paste Special- Special insert >
Paste in Place- Paste instead (Shift+Ctrl+V)
Paste Into Paste in (Alt+Shift+Ctrl+V)
Paste outside- Paste outside
find- Search (Ctrl+F)
Check Spelling- Spellchecking
Find and Replace Text- Find and replace text
Fill- Fill (Shift+F5)
Stroke- Perform stroke
Content-Aware Scale- Scale with content (Alt+Shift+Ctrl+C)
Puppet Warp- Puppet deformation
Perspective Warp- Perspective distortion
Free Transform- Free transform (Ctrl+T)
Transform- Transformation >
Auto Align Layers- Automatically align layers
Auto Blend Layers- Auto overlay layers
Define Brush Preset- define brush
Define Pattern- Define pattern
Define Custom Shape- Define an arbitrary shape
Purge- Delete from memory >
Adobe PDF Presets- Adobe PDF Presets
Presets- Kits >
Remote Connections- Remote connections
Color Settings- Adjust colors (Shift+Ctrl+K)
Assign Profile- Assign profile
Convert to Profile- Convert to Profile
Keyboard Shortcuts- Keyboard shortcuts (Alt+Shft+Ctrl+K)
Menus- Menu (Alt+Shft+Ctrl+M)
Preferences- Settings >
General- Basic (Ctrl+K)
Interface- Interface
sync settings- Sync settings
File Handling- File handling
Performance- Performance
Scratch Discs- Working disks
Cursors- Cursors
Transparency & Gamut- Transparency and color gamut
Units & Rulers- Units and rulers
Guides, Grid & Slices- Guides, grid and slices
plug-ins- External modules
type- Text
Enhanced Controls- Advanced controls
Technology previews- Technology views
Image - Image
mode- Mode
bitmap- Bit format
grayscale- Grayscale
Duotone- Duplex
indexed color- Indexed colors
RGB color- RGB
CMYK color- CMYK
Lab Color-Lab
Multichannel- Multichannel
8 Bits (Channel)- 8 bits (channel)
16 Bits (Channel)- 16 bits (channel)
32 Bits (Channel)- 32 bit (channel)
color table- Color Chart
Adjustments- Correction
Brightness/Contrast- Brightness/Contrast
Levels- Levels (Ctrl+L)
Curves- Curves (Ctrl+M)
exposure- Exposure
Vibrance- Juiciness
Hue/Saturation- Hue/Saturation (Ctrl+U)
color balance- Color balance (Ctrl+B)
black & white- Black and white (Alt+Shift+Ctrl+B)
Photo Filter- Photo filter
Channel Mixer- Channel mixing
color lookup- Color search
Invert- Invert (Ctrl+I)
posterize- Posterization
Threshold- Threshold
Gradient Map- Gradient map
selective color- Selective color correction
Shadows/Highlights- Shadows/Lights
HDR Toning- HDR toning
Variations- Options
Desaturate- Desaturate (Shift+Ctrl+U)
Match Color- Pick up color
Replace Color- Replace color
Equalize- equalize brightness
Auto tone- Autotone (Shift+Ctrl+L)
Auto Contrast- Auto contrast (Alt+Shift+Ctrl+L)
Auto Color- Automatic color correction (Shift+Ctrl+B)
Image Size- Image size (Alt+Ctrl+I)
Canvas Size- Canvas Size (Alt+Ctrl+C)
Image Rotation- Image Rotation >
Crop- Crop
trim- Trimming
Reveal All- Show all
Duplicate- Create duplicate
Apply Image- External channel
Calculations- Calculations
Variables- Variables >
Apply Data Set- Apply dataset
Trap- Trapping
analysis- Analysis >
Layer - Layers
New- New
layer- Layer (Shift+Ctrl+N)
Layer from background- Layer from background
group- Group
Group from Layers- Group of layers
Layer Via Copy- Copy to new layer (Ctrl+J)
Layer Via Cut- Cut to new layer (Shift+Ctrl+J)
Copy CSS- Copy CSS
Duplicate Layer- Duplicate layer
Delete- Delete >
Rename Layer- Rename layer
layer style- Layer style
Blending Options- Overlay options
Bevel & Emboss- Embossing
Stroke- Stroke
Inner Shadow- Inner shadow
Inner Glow- Inner glow
Satin- Gloss
color overlay- Color overlay
gradient overlay- Gradient overlay
pattern overlay- Pattern overlays
Outer Glow- External glow
Drop Shadow- Shadow
Copy Layer Style- Copy layer style
Paste Layer Style- Paste layer style
Clear Layer Style- Clear layer style
global light- Global Illumination
Create layer- Form a layer
Hide All Effects- Hide all effects
Scale Effects- Impact layer effects
Smart Filter- Smart filter >
New Fill Layer- New fill layer
solid color- Color
Gradient- Gradient
pattern- pattern
New Adjustment Layer- New adjustment layer
Brightness/Contrast- Brightness/Contrast
Levels- Levels
Curves- Curves
exposure- Exposure
Vibrance- Juiciness
Hue/Saturation- Hue/Saturation
color balance- Color balance
black & white- Black and white
Photo Filter- Photo filter
Channel Mixer- Channel mixing
color lookup- Color search
Invert- Inversion
posterize- Posterization
Threshold- Isohelia
Gradient Map- Gradient map
selective color- Selective color correction
Layer Content Options- Layer content options
layer mask- Layer mask
Vector Mask- Vector Mask >
Create Clipping Mask- Create Clipping Mask (Alt+Ctrl+G)
Smart Objects- Smart Object >
Video Layers- Video Layers >
Rasterize- Rasterize >
New Layer Based Slice- New fragment from the layer
Group Layers- Group layers (Ctrl+G)
Ungroup Layers- Ungroup layers (Shift+Ctrl+G)
hide layers- Hide layers
Arrange- Organize >
Combine Shapes- Merge Shapes >
Align- Align >
distribution- Distribute >
Lock All Layers in Group- Lock all layers in a group
Link Layers- Link layers
Select Linked Layers- Select related layers
Merge Down- Merge with previous (Ctrl+E)
Merge Visible- Merge visible (Shift+Ctrl+E)
flatten image- Perform mixing
Matting- Edge processing >
Type - Text
panels- Panels >
Anti Alias- Smoothing >
Orientation- Orientation
Horizontal- Horizontal
Vertical- vertical
open type-opentype>
Extrude to 3D- Extrude in 3D
Create Work Path- Create work path
Convert to Shape- Convert to curves
Rasterize Type Layer- Rasterize text layer
Convert to Paragraph Text- Convert to block text
Warp Text- Warp text
Font Preview Size- Viewed font size >
Language Options- Language Options >
Update All Text Layers- Update all text layers
Replace All Missing Fonts- Replace all missing fonts
Paste Lorem Ipsum- Paste Lorem Ipsum
Load Default Type Style- Load default font styles
Select - Selection
All- All (Ctrl+A)
Deselect- Deselect (Ctrl+D)
Reselect- Select again (Shift+Ctrl+D)
inverse- Invert (Shift+Ctrl+I)
All Layers- All layers (Alt+Ctrl+A)
Select Layers- Deselect layers
Find Layers- Find Layers (Alt+Shift+Ctrl+F)
Isolate Layers- Isolate layers
color range- Color range
focus area- Focus area
subject- Thing
Select and Mask- Selection and mask (Alt+Ctrl+R)
Modify- Modification
Border- The border
Smooth- Smoothen
Expand- Expand
contract- Compress
Feather- Feather (Shift+F6)
Grow- Adjacent pixels
Similar- similar shades
Transform Selection- Transform selected area
Edit in Quick Mask Mode- Edit in quick mask mode
Load Selection- Download selected area
New 3D Extrusion- New 3D extrusion
Filter - Filter
Last Filter- Last filter (Alt+Ctrl+F)
Convert for Smart Filters- Convert to smart filters
Filter Gallery- Filter Gallery
Adaptive Wide Angle- Adaptive wide angle (Alt+Shift+Ctrl+A)
Lens Correction- Distortion correction (Shift+Ctrl+R)
Liquify- Plastic
Vanishing Point- Correct perspective (Alt+Ctrl+V)
Blur- Blur
field blur- Field blur
Iris Blur- Aperture blur
tilt-shift- Tilt-shift
Average- The average
Blur- Blur
Blur More- Blur +
Box Blur- Frame blur
Gaussian Blur- Gaussian blur
lens blur- Blur at shallow depth of field
motion blur- Motion blur
Radial Blur- Radial blur
shape blur- Shape blur
Smart Blur- "Smart" blur
Surface Blur- Surface blur
Distort- Distortion
wave- Wave
Pinch- Distortion
ZigZag- Zigzag
Shear- Curvature
Polar Coordinates- Polar coordinates
Ripple- Ripples
Twirl- Twisting
Displace- Offset
Spherize- Spherization
noise- Noise
Add Noise- Add noise
Despeckle- Retouch
Dust & Scratches- Dust and scratches
Median- Median
reduce noise- Reduce noise
Pixelate- Registration
Color Halftone- Color halftones
crystallize- Crystallization
Facet- Facet
Fragment- Fragment
Mezzotint- Mezzotint
Mosaic- Mosaic
Pointillize- Pointillism
Render- Rendering
clouds- Clouds
Difference Clouds- Overlay clouds
fibers- fibers
Lens Flare- Glare
Lighting Effects- Lighting effects
Sharpen- Sharpening
Shake reduction- Image stabilization
Sharpen- Sharpening
Sharpen Edges- Sharpness at the edges
Sharpen More- Sharpness +
smart sharpen- "Smart Sharpen
unsharp mask- contour sharpening
Style- Styling
diffuse- Diffusion
Emboss- Embossing
extrude- Extrusion
Find Edges- Edge selection
Glowing Edges- Glow edges
solarize- Solarization
Tiles- Splitting
Trace Contour- Contour tracing
Wind- Wind
oil paint- Oil paint
video- Video >
Other- Other >
Browse Filters Online- Find filters online
3D
New 3D Layer from File- Create 3D layer from file
Merge 3D Layers- Merge 3D layers
Export 3D Layer- Export 3D layer
Get More Content- Get more content
New 3D Extrusion from Selected Layer- New 3D extrusion from selected layer
New 3D Extrusion from Selected Path- New 3D extrusion from selected path
New 3D Extrusion from Current Selection- New 3D extrusion from current selection
New Mesh from Layer- New mesh from layer
Group Objects- Group objects
Group All Objects in Scene- Group all objects in the scene
Move Object to Ground Plane- Move object to ground plane
New Tiled Painting from Layer- New mosaic picture from layer
Generate UVs- Create UV
Paint Falloff- Corner fading
paint system- Drawing system
Paint on Target Texture- Colorize on target texture
Select Paintable Areas- Select areas to paint
Create Painting Overlay- Create picture overlay
split extrusion- Split extrusion
Apply Cross Section to Scene- Apply cross section to scene
Unify Scene for 3D Printing- Unify the scene for 3D printing
Add Constraints from- Add limits from
Show/Hide Polygons- Show/hide polygons
Make Work Path from 3D Layer- Create work path from 3D layer
Render- Rendering (Alt+Shift+Ctrl+R)
Sketch With Current Brush- Sketch with the current brush
Print Settings- 3D printing settings
3D printing- 3D printing
Cancel 3D Print- Cancel 3D printing
3D Print Utilities- 3D printing utilities
View - View
Proof Setup- Proof Options >
Proof Colors- Color Proof (Ctrl+Y)
Gamut Warning- Warning when going beyond the color coverage (Shift+Ctrl+Y)
Pixel Aspect Ratio- Pixel aspect ratio >
Pixel Aspect Ratio Correction- Correction of proportions
32-bit Preview Options- 32-bit viewing options
zoom in- Zoom in (Ctrl++)
zoom out- Zoom Out (Ctrl+-)
Fit on Screen- Show in full screen (Ctrl+0)
100% - 100% (Ctrl+1)
Print Size- Print size
Screen Mode- Screen Modes >
Extras- Auxiliary elements (Ctrl+H)
show- Show
Layer Edges- Layer border
Selection Edges- Borders of selected areas
Target Path- Target path (Shift+Ctrl+H)
Grid- Grid (Ctrl+")
Guides- Guides (Ctrl+;)
Count- Counting
Smart guides- Quick guides
Slices- Fragments
notes- Comments
Pixel Grid- Pixel grid
3D Secondary View- Secondary 3D view
3D Ground Plane- 3D base plane
3D Lights- 3D light
3D Selection- 3D selection
UV Overlay- UV overlay
brush preview- Brush preview
mesh- Net
Edit Pins- Edit pins
All- Everything
None- Remove selection
Show Extra Options- Auxiliary elements
Rulers- Rulers (Ctrl+R)
Snap- Snap (Shift+Ctrl+;)
Snap To- Bind to
Guides- guiding
Grid- grid lines
Layers- Layers
Slices- Fragments of cutting
Document Bounds- Document borders
All- Everything
None- Remove selection
lock guides- Lock guides (Alt+Ctrl+;)
Clear Guides- Remove guides
New Guide- New guide
Lock Slices- Pin fragments
Clear Slices- Delete fragments
Window - Window
Arrange- Organize >
Workspace- Working environment >
Extensions- Extensions
3D
Actions- Operations / Alt+F9
Adjustments- Correction
Brush- Brush / F5
Brush Presets- Brush sets
Channels- Channels
character- Symbol
Character Styles- Character styles
clone source- Source of Clones
color- Color / F6
Histogram- Bar graph
History- Story
info- Info / F8
Layer Comps- Layer compositions
Layers- Layers / F7
measurement log- Measurement log
Navigator- Navigator
notes- Comments
paragraph- Paragraph
Paragraph Styles- Paragraph styles
Paths- Contours
Properties- Properties
styles- Styles
Swatches- Samples
Timeline- Timeline
Tool Presets- Tool presets
Options- Parameters
Tools- Tools
Toolbar
MoveTool- Move tool (V)
Auto Select: Group- Auto select: Group
Auto Select: Layer- Auto select: Layer
Show Transform Controls- Show ex. elem.
Align top edges- Top alignment
Align vertical centers- Center Alignment Vertically
Align bottom edges- Bottom alignment
Align left edges- Left alignment
Align horizontal centers- Alignment of centers horizontally
Align right edges- Right alignment
Distribute top edges- Distribution of top edges
Distribute vertical centers- Distribution of centers vertically
Distribute bottom edges- Distribution of bottom edges
Distribute left edges- Distribution of left edges
Distribute horizontal centers- Distribution of centers horizontally
Distribute right edges- Distribution of right edges
Auto Align Layers- Automatic alignment of layers
Rotate the 3D Object- Rotate 3D object
Roll the 3D Object- Rotate 3D object
Drag the 3D Object- Drag 3D object
Slide the 3D Object- Slide a 3D object
Scale the 3D Object- Scale 3D object
Rectangular Marquee Tool- Rectangle Marquee Tool
New Selection- New highlighted area
Add to selection
Subtract from selection- Subtraction from selection
Intersect with selection- Intersect with selection
Feather- feathering
Style: Normal- Style: Plain
Style: Fixed Ratio- Style: Preset proportions
Style: Fixed Size- Assigned. the size
Width- Width
Height- Height
Refine Edge- Specify. edge
Elliptical Marquee Tool- Oval Marquee Tool
New selection- New highlighted area
Add to selection- Add to selection
Subtract from selection
Intersect with selection
Feather- feathering
Anti-alias- Smoothing
Style: Normal- Style: Plain
Style: Fixed Ratio- Assigned. proportions
Style: Fixed Size- Style: Preset the size
Width- Width
Height- Height
Refine Edge- Specify. edge
Single Row Marquee Tool- Tool "Region (horizontal line)"
New Selection- New highlighted area
Add to selection- Add to selection
Subtract from selection- Subtraction from selection
Intersect with selection- Intersect with selection
Feather- feathering
Single Column Marquee Tool- Tool "Region (vertical line)"
New selection- New highlighted area
Add to selection- Add to selection
Subtract from selection- Subtraction from selection
Intersect with selection- Intersect with selection
Feather- feathering
Lasso Tool-Lasso tool
New selection- New highlighted area
Add to selection- Add to selection
Subtract from selection- Subtraction from selection
Intersect with selection
Feather- feathering
Anti-alias- Smoothing
Refine Edge- Specify. edge
Polygonal Lasso Tool- Straight Lasso Tool
New selection- New highlighted area
Add to selection- Add to selection
Subtract from selection- Subtraction from selection
Intersect with selection- Intersection with selected region.
Feather- feathering
Anti-alias- Smoothing
Refine Edge- Specify. edge
Magnetic Lasso Tool- Magnetic Lasso Tool
New selection- New highlighted area
Add to selection- Add to selection
Subtract from selection- Subtraction from selection
Intersect with selection- Intersection with selected area
Feather- feathering
Anti-alias- Smoothing
Width- Width
contrast- Contrast
Frequency- Frequency
Use Tablet pressure to change pen width- Change. pressure leads to change. width
Refine Edge- Specify. edge
Quick Selection Tool- Quick Selection Tool
New selection- New highlighted area
Add to selection- Add to selection
Subtract from selection- Subtraction from selection
brush picker- Brush Options
Sample All Layers- Sample from all layers
Auto Enhance- Amplify automatically
Refine Edge- Specify. edge
Magic WandTool- Magic wand tool
New selection- New highlighted area
Add to selection- Add to selection
Subtract from selection- Subtraction from selection
Intersect with selection- Intersection with selected area
Sample Size: Point Sample- Sample size: Dot
Sample Size: 3 by 3 Average- Sample size: Medium 3 x 3
tolerance- Tolerance
Anti-alias- Smoothing
contiguous- Adjacent. pix
Sample All Layers- Sample from all layers
Refine Edge- Specify. edge
crop tool(Frame Tool /C)
Perspective Crop Tool(Perspective Crop Tool / C)
slice tool(Pattern Tool / C)
Slice Select Tool(Slice Tool / C)
Eye Drop Tool(Pipette Tool / I)
3D Material Eyedropper Tool(3D Material Eyedropper Tool / I)
Color Sampler Tool(Color Target Tool / I)
Ruler Tool(Ruler Tool / I)
note tool(Comment Tool / I)
CountTool(Counter Tool / I)
Spot Healing Brush Tool(Spot Healing Brush Tool / J)
Healing Brush Tool(Healing Brush Tool / J)
patch tool(Patch Tool / J)
Content-Aware Move Tool(Content-Aware Move Tool / J)
Red Eye Tool(Red Eye Tool / J)
brush tool(Brush Tool / B)
Pencil Tool(Pencil Tool / B)
Color Replacement Tool(Color Replacement Tool)
Mixer Brush Tool(Mix Brush Tool)
Clone Stamp Tool(Stamp Tool / S)
Pattern Stamp Tool(Pattern Stamp Tool / S)
History Brush Tool(Archive Brush Tool / Y)
Art History Brush Tool(Archival Art Brush Tool / Y)
Eraser Tool(Eraser Tool / E)
Background Eraser Tool(Background Eraser Tool / E)
Magic Eraser Tool(Magic Eraser Tool / E)
Gradient Tool(Gradient Tool / G)
Paint Bucket Tool(Fill Tool / G)
3D Material Drop Tool(3D Material Selector / G)
Blur Tool(Blur Tool)
sharpen tool(Sharpen Tool)
Smudge Tool(Finger tool)
DodgeTool(Dodge Tool / O)
BurnTool(Dimmer Tool / O)
SpongeTool(Sponge Tool / O)
pen tool(Pen Tool / P)
Freeform Pen Tool(Free Pen Tool / P)
Add Anchor Point Tool(Pen+ tool (add anchor point))
Delete Anchor Point Tool(Pen Tool- (delete anchor point))
Convert Point Tool(Corner tool)
Horizontal Type Tool(Horizontal Type Tool / T)
Vertical Type Tool(Vertical Text Tool / T)
Horizontal Type Mask Tool(Horizontal Mask Text Tool / T)
Vertical Type Mask Tool(Vertical Text Mask Tool / T)
Path Selection Tool(Path Selection Tool / A)
Direct Selection Tool(Node Selection Tool / A)
Rounded Rectangle Tool(Rounded Rectangle Tool / U)
Ellipse Tool(Ellipse Tool / U)
Polygon Tool(Polygon Tool / U)
line tool(Line Tool / U)
Custom Shape Tool(Freeform Shape Tool / U)
hand tool(Hand Tool / H)
Rotate View Tool(Rotate View Tool / R)
zoom tool(Zoom Tool / Z)
Default Foreground and Background Colors(Default foreground and background color/D)
Switch Foreground and Background Colors(Switching foreground and background colors / X)
Set foreground color(Choosing the main color)
Set background color(Choose a background color)
Edit in Quick Mask Mode(Editing in Quick Mask / Q mode)
Change Screen Mode(Screen display mode change / F)
Standard Screen Mode(Standard window / F)
Full Screen Mode With Menu Bar(Full screen with main menu / F)
Full Screen Mode(Full screen)
Blending options (Overlay options)
General Blending- Main settings
Blend Mode- Overlay mode
Normal- Basic
Dissolve- Attenuation
Darkens- Dimming
Multiply- Multiplication
color burn- Shading the base
Linear Burn- Linear dimmer
darker color- Darker
lighten- Light replacement
Screen- Screen
color dodge- Lightening the base
Linear Dodge- Add- Linear light. (add)
Lighter Color- Lighter
overlay- overlap
soft light- Soft light
hard light- hard light
Vivid Light- Bright light
Linear Light- Linear light
pin light- Spot light
hard mix- Rigid mixing
Difference- Difference
Exclusion- An exception
Subtract- Subtraction
Divide- Divide
Hue- Color tone
Saturation- Saturation
color- Chroma
Luminosity- Brightness
Opacity- Opacity
Fill Opacity- fill opacity
Channels RGB- RGB channels
Knockout: None- Translucent: Do not show
Knockout: Shallow- Translucent: Fine
Knockout: Deep- Translucent: Deep
Blend Interior Effects Group- Overlay internal effects as a group
Blend Clipped Layers as Group- Overlay clipping layers as a group
Transparency Shapes Layer- Shape layer transparency
Layer Mask Hides Effects- Layer mask hides effects
Vector Mask Hides Effects- Vector mask hide effects
Blend If: Gray- Overlay if: Gr. ser.
Blend If: Red- Overlay if: Red
Blend If: Green- Overlay if: Green
Blend If: Blue- Overlay if: Blue
This Layer- This layer
underlaying layer- Underlying layer
Layer Style - Layer style
Bevel & Emboss- Embossing
Bevel & Emboss-Contour- Embossing - Contour
Bevel & Emboss - Texture- Embossing - Texture
Stroke- Stroke
Inner Shadow- Inner shadow
Inner Glow- Inner glow
Satin- Gloss
color overlay- Color overlay
gradient overlay- Gradient overlay
pattern overlay- Pattern overlay
Outer Glow- External glow
Adobe Photoshop has a great feature - it's changing the blend mode of layers. Today we will talk about Color Burn and Color Dodge. These blend modes provide some very interesting possibilities. Using these blend modes changes the look of the image significantly, so you need to work very smoothly and carefully.
color burn
The Color Burn mode darkens the black point by the value of the brightness of the overlay layer.
1. What is the neutral color for this mode?
- For the Color Burn mode, the neutral color is white.
2. What does the Color Burn blending mode have the most effect on?
- To a greater extent, it affects the shadows, making them darker. The saturation of the image in this mode changes to a lighter side.
3. How does the contrast change happen?
- The contrast throughout the image is increased. Because of this, the details in the shadows become completely dark. There is a gap in the shadows.
- To bring back detail in the shadows, you need to use a mask, limiting the adjustment layer to affect only the bright parts of the image, and excluding its effect on areas where failure may occur.
4. How does the impact of a layer decrease as the opacity decreases?
The impact is uneven. In the right diagram, you can see how the effect of the element with brightness 64 decreases as the transparency decreases. On the left diagram you can see the reduction in exposure by simple clarification.
Reducing the opacity allows you to partially restore the details of the original image that are in the shadows.
5. What happens if you overlay an image on itself?
- The white point of such a picture will remain in place, but the darkening of the midtones will increase as they decrease in brightness.
Applying Color Burn Mode
Increasing the contrast and saturation of light objects

The Color Burn mode increases contrast in highlights and enhances color saturation. Let's try to make the deer juicier. In order not to change the color tone, you need to work with a neutral gray color.

Create a new empty layer by pressing Alt + click on the button for creating a new layer. In the settings, set the blending mode to Color Burn. Set the color of the layer to white, and reduce the opacity to 75% so that there is no clipping of details in the shadows.

On the created layer, draw the necessary areas with a neutral gray color. This is what the image looked like after processing:

The result is an analogue of the Burn Tool. Here's what flexibility is:

You can draw with a brush with low transparency. This will allow you to make changes more smoothly. Each next stroke will intensify the impact, and if suddenly the impact is too strong, you can switch to white and weaken it.

You can also set the brush's opacity to 100% and choose a light gray color. In this case, a strictly limited effect will be introduced, which will not depend on the number of strokes.
Removing haze and glare

In this example, the mountain is covered with a blue haze.
First you need to choose the color that will be adjusted.

Correction must be made in the opposite color. To recognize it, you need to take a color sample with a pipette and change it by 180 °. For blue, the reverse is yellow. You can get the reverse color by decreasing the H° value by 180°. Saturation is controlled by the S (Saturation) value. For this case, it should be reduced to a value of 20%.
The darker our adjustment color is, the more it will affect the original image. Therefore, the B (Brightness) setting should be set to between 80% and 100%.

Good flexibility in processing can be obtained by working with adjustment layers of bays. For our method, it is imperative that there is a white substrate, and on it there is already a drawing in a corrective color. Therefore, we create a group in which we lay down a white fill adjustment layer. Above it is the same layer, only with a yellow fill (the color that we got earlier). You will need to draw with masks.
Change the group's blend mode to Color Burn and reduce its opacity to 75%. Now fill the mask of the yellow adjustment layer with black and paint over it with a white brush. Additional corrective colors can be added as needed.


For effectively darkening relatively dark areas when creating masks
Color Burn has little effect on the light areas, but greatly changes the dark ones. This feature can be used to darken shadows. This is useful when light areas need to be left untouched.

Now we will create a mask for the flower. Channels will serve as the basis of the mask. The red channel is great for creating a mask, but there is little separation between the petals and the dark part of the picture. Excellent separation is observed in the green channel.

Curves should be applied to the channels with the parameters shown in the screenshot.

The overlay will be done using Channel Mixer adjustment layers. The point is to create a monochrome image from the red channel on the Gray_from_Red layer.

The Green_to_Red layer below it overlays the green channel on top of the red.


You can see on the basis of the experiment how much more profitable in this case the use of Color Burn than Multiply. The Multiply blend mode left a lot of detail on the leaves and in the background.
color dodge
Color Dodge shifts the white point to the left by the brightness value of the overlay image.
1. What is the neutral color in this mode?
- For all brightening modes, black is the neutral color.
2. What is more affected by this mode?
- The maximum effect is on light. As the image darkens, the exposure decreases to zero at the black point.
3. How does the contrast change?
- Contrast drops to zero at the brightest point and decreases as it gets darker.
4. How does the effect of the blending mode change depending on the opacity of the overlay layer?
- Decreasing opacity is not the same as reducing influence. On the left is how the effect changes as the overlay is lightened, and on the right as the opacity decreases.

- Lowering the opacity partially restores highlight detail in the original image.
6. What happens if you overlay a picture on itself?
- Three such blending conditions will leave the black point unchanged, but as the tones lighten, they will become lighter. Clipping of bright tones can occur in the brightest places. They will look like overexposure.
Applying the Color Dodge Mode
Pulling objects from shadows

This example will be disassembled without details, since everything here is similar to the previous section on using the Color Burn blend mode. In the photo in question, red vegetation should be pulled out of the shadow.

We take the color of the plant with a pipette. We will strengthen it. Since the color (Hue) should not be changed, this parameter is left unchanged. Brightness (Brightness) should be reduced, because Color Dodge reacts very sharply to this parameter. Since the brightness is low, and we need to "light" the vegetation, we need to increase the saturation (Saturation).

With a mask, draw the area in which the plants are located.

It is worth paying attention to the fact that the drawn mask captures not only the areas that need to be adjusted, but also neighboring elements. However, they are not subject to change. This can be seen in the last underwater vegetation example and in the mountain haze example. All this is due to the specific algorithm of these blending modes.
Yellow-orange with the Color Burn blending mode brings changes only to the blue and green channels. The sky is too pale, so the changes that have affected it are so minor that they are invisible to the eye. In Color Dodge mode, red brings the maximum change to the red channel only. Water and other algae are too dark and therefore do not change in the visible spectrum.
Based on materials from the site:
Material Sponsor.
Today, the purchase of a child car seat is often the main purchase for a newly born baby. After all, the primary task of parents is to pick up the baby from the maternity hospital and bring him home by car. You can buy a child car seat in the AKBkids online store. Free shipping across Ukraine.
Good afternoon friends, I have already published articles-manuals on Photoshop (and a description of all).
Now I want to start a series of posts in which I will describe all the main features of the Layer Styles window or “layer styles” in Russian. 
All these styles and effects are probably the most used by any web designer, so knowing all the basic features is a must, especially for beginners. As you can see in the screenshot, there are quite a few styles, and for each I will try to make a separate detailed post, in total, according to my calculations, I will get 10-11 posts, starting from Drop Shadow and ending with Stroke. Maybe I will combine something or, on the contrary, I will divide it, it will be seen in the future, but for now the first post from the cycle about Color Overlay. Go!
I want to note right away - I always use the English version of Photoshop and therefore I take all my screenshots in this form and I am not going to translate the name of the styles into Russian. By the way, I have always said and will say - work on the English version, because all good manuals, source codes and documentation are created specifically for English versions. It’s easier to learn new things this way, since there is almost no sensible information in Runet.
Using Color Overlay
Color Overlay literally translates from English as “color overlay” or “color blending”, it is already clear from the name that the main function of this style is working with color, mixing different colors of the layer with the background, etc.
The Color Overlay style is pretty easy to use and has only two settings - Blend Mode and Opacity.
Blend Mode- is the main feature of Color Overlay, it has 25 color blending modes, using which we can create various color effects.

All "blend modes" are divided into basic types of effects on layers and colors:
| Modes | Meaning | Mode Type |
| Normal | normal, normal state | Basic (Basic Modes) |
| Dissolve | The combination of the top layer with the bottom, due to the special. pattern. If the top layer has 100% opacity, then the effect will not be visible. | |
| Darkens | Compares two layers and darkens the light pixels on one layer and the dark pixels on the other layer. | Darken Group (Darken Modes) |
| Multiply | Multiplies the top layer pixel with the corresponding number of bottom layer pixels. The result is a darker image. | |
| color burn | Creates a darker image with a higher level of contrast. If the top layer is white, then no change will be visible. | |
| Linear Burn | A more "powerful" mix of Color Burn and Multiply blending modes, most of the dark pixels are converted to black. | |
| darker color | Only dark pixels remain in the visible part of the image | |
| lighten | The complete opposite of the Darken blend mode | Lightening group (Lighten Modes) |
| Screen | Multiplies the background of the two layers towards lighter pixels. The effect is similar to projecting several photographic slides at the same time. | |
| color dodge | Lightens the layer. If the top layer is black, then there will be no effect. | |
| Linear Dodge (Add) | It's a mixture of Color Dodge and Screen modes. Light pixels are converted to even lighter ones. | |
| Lighter Color | Compares the color modes of all layers and displays the lightest pixels. | |
| overlay | this mode simultaneously brightens the light pixels (Screen mode) and darkens the dark pixels of the layers (Multiply). | Contrast Modes |
| soft light | A mixture of Burn and Dodge modes. Image contrast increases slightly more than the Overlay mode. | |
| hard light | A stronger variation of Overlay. | |
| Vivid Light | It all depends on the color of the top layer. If it is lighter than 50% gray, then the contrast decreases (Color Burn), if vice versa, the contrast increases |
|
| Linear Light | The principle of operation is similar to Vivid Light, only instead of contrast, there is an increase or decrease in brightness | |
| pin light | A combination of Lighten and Darken overlay styles that replace pixel colors. | |
| hard mix | A heavy mix of colors - light ones are darkened, dark ones are lightened. | |
| Difference | Similar pixels combined into one color | Comparative Modes |
| Exclusion | Similar to Difference, only less contrast for the converted layers. | |
| Hue | Combines saturation (Saturation) and glow (Luminance) of the lower layer with the color palette of the upper one. | Composite Modes |
| Saturation | The same as Hue, only the saturation (Saturation) of the upper layer is compared. | |
| color | Matches the saturation and hue of the top layer with the luminosity level of the bottom layer | |
| Luminosity | The exact opposite of the "Color" blend mode |
In the example below, you can see how the blending of the top layer with the background changes depending on the selected mode.
blending modes) determine how the top layer interacts with the layer directly below it. Blending modes make it easier and faster to change shades, remove imperfections, and perform a number of other operations. In Photoshop, all modes are divided into functional groups: Basic Modes, Darken Modes, Lighten Modes, Contrast Modes, Comparison Modes and Component Modes.
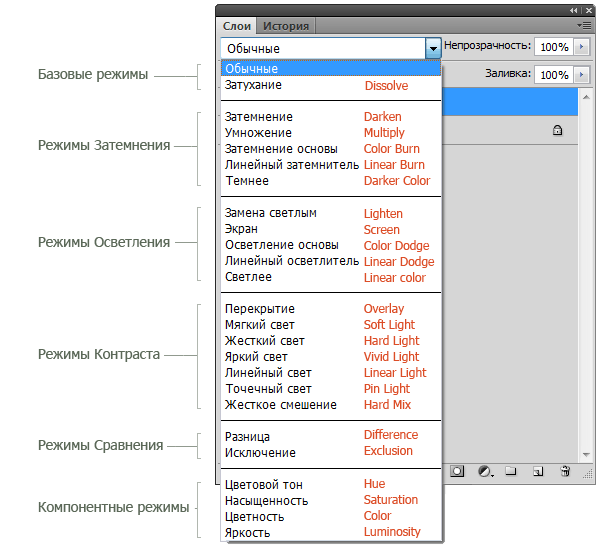
Layer blend modes are in the drop-down menu at the top of the Layers panel ( Layers). In the figure, for convenience, I wrote the name of the mode in English in red font.
1. Basic modes
Normal (Normal) is the default layer mode. Top layer pixels are opaque and images do not interact. As an example, we will consider the blend modes in these two pictures. 

attenuation (Dissolve) uses a pixel pattern. Gives a porous effect. The effect will appear only when the transparency of the top layer is less than 100%. Here the transparency is 20%. 
2. Dimming modes
Blackout (Darkens) - leaves only the dark areas of the image visible. Blends pixels where the top layer is darker than the bottom layer. 
Multiplication (Multiply) - allows you to darken the entire image and is useful in situations where you need to increase the density of highlights and mid-tones. It is especially useful when working with overexposed or too light images. 
Base darkening (color burn) - darkens dark colors and tints without affecting light tints. 
Linear dimmer (Linear Burn) - Uses the same approach as Color Burn, but produces a stronger darkening effect. If the top layer is white, there will be no change. 
Darker (darker color) - similar to the Burn mode, except that it works on all layers at once, and not on one. When you blend two layers, only the dark pixels will remain visible. 
3. Lightening modes
Light replacement (lighten) - compares the colors of the top and bottom layers and blends pixels if the top layer is lighter than the bottom. 
Screen (Screen) - allows you to lighten the entire image and is useful in situations where you need to "show" any areas in underexposed images. 
Base lightening (color dodge) - Opposite of Color Burn, brightens light colors and tints without affecting dark areas of the image. 
Linear Dodge (Linear Dodge) - Allows you to lighten the image, but unlike the Screen mode, it clips the values and produces sharper results than the Screen or Color Dodge blend mode. 
Lighter (Linear Color) - similar to the Lighten mode, only works with all layers at the same time, instead of one layer. When you blend two layers together, only the light pixels will remain visible. 
4. Contrast modes
overlap (overlay) - combines the effect of the Multiply and Screen modes, blending the top layer with the bottom. If the top layer is 50% gray, there will be no effect. 
Soft light (soft light) - Similar to Overlay, but with a more moderate effect. If the top layer is 50% gray, there will be no effect. 
hard light (hard light) - Uses the same approach as the Overlay mode, but the effect is stronger. Here, the top layer is subject to either "Screen" or "Multiply" mode, depending on its color. If the top layer is 50% gray, there will be no effect. 
Bright light (Vivid Light) - Combines the effect of Color Burn and Color Dodge, and applies blending based on the color of the top layer. If the top layer is 50% gray, there will be no effect. 
Linear light (Linear Light) - Similar to Bright Light mode, but with a stronger effect. If the top layer is 50% gray, there will be no effect. 
spot light (pin light) blends light colors using the Lighten mode and dark colors using the Burn mode. If the top layer is 50% gray, there will be no effect. 
Rigid mixing (hard mix) - creates a picture with even tones, limited in colors and posterized. The glow of the top layer is blended with the color of the bottom. 
5. Comparison modes
Difference (Difference) - Displays the tonal difference between two layers by removing light pixels from either layer. The result is a dark and sometimes inverted picture. 
An exception (Exclusion) - similar to the Difference mode, but with a less extreme effect. 
5. Component modes
Color tone (Hue) - combines the color of the top layer and the color variation and tone of the bottom layer. 
Saturation (Saturation) - Combines the color variation of the top layer with the color and tone of the bottom layer. 
Chroma (color) - combines the color and color variation of the top layer with the tone of the bottom layer. 
Brightness (Luminosity) - combines the tone of the top layer and the color and color variation of the bottom layer.