Quite often, Windows users complain that when there is a large amount of RAM, the value available for use is not at all the value that is determined by the operating system itself. For some, this may be 35-50 MB, but you can find values \u200b\u200band much higher (hardware reserved memory). How to remove further and will be considered. But for now, let's focus on the root causes of this situation. Why is memory reserved, for what resources?
Memory (hardware reserved): how to remove and what is the cause of this problem?
First of all, any user of the Windows family of operating systems should clearly understand that this problem is typical only for systems with a 32-bit architecture or, as it is usually referred to, x86. In 64-bit operating systems, this question does not arise at all.
As for the reasons that, when viewing the available volume, it turns out that the memory is reserved by hardware (how to remove the existing reserve in Windows 7, we will consider a little later), they are mainly associated not even with the operating system processes themselves, but with the release of memory for integrated graphics accelerators , mounted directly on the motherboard, which cannot provide enough memory to perform any system and non-system operations related to displaying current events on the screen in terms of the correct operation of the system interface itself.
In addition, it is not uncommon for RAM to be distributed in accordance with user settings, where the system partition indicates the use of all processor cores with the maximum RAM allocated to each core. But the main problem with setting such options is that not everyone is aware of exactly how many cores a processor has and what memory to allocate for each of them. For example, many people think that second-generation Intel Core i7 processors found in laptops are quad-core. This is not true. Calling them such can be very arbitrary, since there are two streams of computing power for each core. By installing memory for four processors / cores instead of two, you get the problem that memory is “eaten” in the system properties.
RAM is reserved by hardware: how to remove it? The simplest way to fix the problem
But let's get back to the original problem. To get started, even after the initial installation of the operating system, enter its properties and look at the available amount of RAM in the performance section, compared to the one that is fully determined. If the discrepancy is too large, it is possible that the installed system has its limitations.

At least initially, it is worth looking at the special compatibility tables of system versions with the computer configurations used. It may very well be that the installed OS will have to be changed (no additional actions in this case will have an effect). On 32-bit systems, the ceiling is typically 4 GB. Anything above that will be defined as hardware reserved memory. How to remove (in Windows 10, for example) such nonsense, I think, is already clear. If the system does not support installing more RAM, then there is nothing to try. Change the system or remove the memory bars.
Using System Configurator Settings
With the Windows configurator, which is called by the msconfig command, the situation is somewhat more complicated. This is where the memory allocation settings for each processor core are located.

If you already set such parameters yourself and precisely by means of the system, specify only the main cores without taking into account threads and memory allocation for each core. If you are prompted to specify the maximum memory, do not particularly flatter yourself - the system after a reboot (and it is mandatory after setting the appropriate options) can simply “fly off”, and after that no means of resuscitation will help it (naturally, except for a complete reinstallation).
Best way to solve a problem
In general, it is believed that the problem of how to remove the hardware-reserved memory can be solved quite simply by installing an operating system similar to the previous one, but having a 64-bit architecture.

Here you do not have to deal with additional settings of options. No, you can, of course, try again to set the use of all CPU cores, but believe me, this will not lead to anything good (tested in practice). Therefore, in order to avoid such incidents, it is better to leave an independent choice to the system itself.
Graphics adapters
In addition, if you see that the memory is reserved by hardware (how to remove the reserve is already somewhat clear), pay attention to the fact that two video cards can be installed on the computer.

Try switching from an integrated adapter to a discrete one, using at least the "Device Manager" in the simplest case, where the built-in chip, as is already clear, just needs to be disabled.
Instead of an afterword
As for the rest, you should initially rely on the tables for limiting the used RAM, since failure to comply with such conditions if the system is incompatible with the hardware of the installed equipment can cause such problems in the future, not to mention more serious consequences.
As for the main solution, immediately pay attention to the graphics card, for which the 32-bit OS allocates memory, even for the execution of its own processes, which cannot be executed without using the minimum required volume (the graphical interface simply will not work). And this, in turn, can provoke the appearance of problems of a more serious nature, which will be impossible to eliminate by standard methods.
Read what does Windows memory shrink mean and how to view compressed memory information on your PC. And also, what to do if the computer does not have enough RAM and how to determine how much memory a certain process takes. Windows 10 uses compression to store more data in your system's RAM. In the Windows 10 Task Manager, the “Performance” tab displays information about the size and current memory usage. Among other parameters, it is indicated that part of the memory is compressed. Let's see what this means?
Memory compression is a new feature in Windows 10 that is not available in earlier Windows 8 and 7. At the same time, Linux and MacOS use this feature.
Typically, if your computer has 8 GB of RAM, and running applications and the system itself use 9 GB of data to store in memory, at least 1 GB had to be stored in the swap file on your computer's hard drive. Accessing data in the paging file slows down the speed of individual applications and the system as a whole.
However, using a compression algorithm (same as in a Zip file), the size of the data can be reduced and placed entirely in RAM. For example, the system may leave 6 GB of uncompressed data, and compress 3 GB, so that they actually occupy 1.5 GB. Thus, you will have 7.5 of the 8 GB of RAM occupied.
Are there any downsides to this approach? Yes and no. Data compression and the inverse procedure require certain processor resources. Therefore, not all data is stored compressed, the system compresses only the information that it considers necessary. The operation of compression and decompression itself is much faster than writing and reading data from disk. Therefore, Windows is looking for a compromise between these two approaches.
Why doesn't Windows compress all data?
As we have already discussed, the speed of compressing and decompressing data is much higher than writing and reading data from disk. Working with such data occurs in a fully automatic mode and does not require user intervention, so why does the system not compress all data?
Working with uncompressed data is much faster. If the operating system needs to search through a large amount of data stored in RAM, then the procedure for reading, decoding and inverse encoding of data requires significant processor time. In addition, the system reserves part of the RAM to decompress the necessary memory buffer in case of such a need.
Based on this, Windows tries to store data that is often accessed in an uncompressed form, data that the system accesses less often is compressed or even saved to the paging file.
What to do if the computer does not have enough RAM?
So what should you do if you see that the system is using a large amount of compressed data or is running on a large swap file? The answer is obvious, add more RAM to your PC, it will be the best solution. It's also obvious that it's best to use as fast RAM as your motherboard allows.
A less obvious solution would be to use an SSD drive for the swap file or the system as a whole. Earlier we looked at how to move the swap file to another drive in our video:
Since the read and write speed of an SSD drive is many times higher than a traditional hard drive, the entire system will run faster.
How to View Compressed Memory Information on Your PC
To view information about how much memory is compressed in the system, you must use the Task Manager. To launch it, right-click on the taskbar and select , or press Ctrl + Shift + Esc (for Windows 10, 8) or Ctrl + Alt + Delete (for any Windows) and select .

By default, it starts in an abbreviated form, you need to access the full version. To do this, click the button More in the lower left corner of the window.

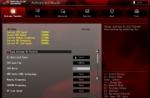
Go to the Performance tab and select Memory from the list on the right. You will see how much memory is compressed in the partition "Use (compressed)". For example, in the screenshot below, Task Manager shows that our system is currently using 4.2 GB, 21.6 MB is compressed memory.
This setting changes constantly depending on the number of applications running and the memory they are using. The amount of compressed memory can also change from the work of system tasks in the background, you can watch this process in real time.

You can also see from the screenshot that our system uses 8GB of DDR3 RAM. 1 GB is reserved by hardware - this memory is used by the integrated graphics system. DIMM memory form factor, 2 brackets are used and 2 more slots in the system are free. The cached 1.9 GB setting displays the current page file size. If you hover your mouse over the diagram in the Memory Structure section, the system will pop up a tooltip with additional information.
How to determine how much memory a certain process takes
For detailed information on the memory that each process takes up, go to the Processes tab, then find the one you need and select it, the memory column will show the actual memory occupied.

Some applications have multiple processes running at the same time, such as Google Chrome. In this case, you need to calculate the sum of the consumed memory of all running processes.
Earlier on our forum, they were interested in the question of how to enable hardware acceleration in DirectX, which allows you to speed up some functions of graphics accelerators and run games that refuse to work on a PC before. This time we will consider the topic of how to enable hardware acceleration of the video adapter on Windows 10 or deactivate this option.
Step-by-step instructions for enabling and disabling hardware acceleration in Windows 10
The first way to disable hardware acceleration of a video adapter in Windows 10 is described in detail on the official Microsoft forum. Let's consider it step by step:
- Right-click on an empty spot on the desktop and select Display Settings.
- A new window will open. Click on the "Advanced Options" link.
- We need the "Diagnostics" tab. In it, click on the "Change settings" button.

- By clicking on this button, a window will appear in which it will be possible, by dragging the slider to the desired position, to activate or deactivate hardware acceleration in Windows 10.
IMPORTANT! If the "Change settings" option is not active, then the ability to enable / disable hardware acceleration is not available on your PC due to the technical characteristics of your device. Or, hardware acceleration is already enabled.
If the hardware acceleration of sound and video in Windows 10 adversely affects the operation of games, programs and the system as a whole, you can disable it using a special registry tweak. To do this, do the following:
- Open notepad. Insert the following text into it:
"DisableHWAcceleration"=dword:00000001
- We save the file under any name, only with the .reg extension.

- We launch the finished file.
- After making changes to the registry, the system must be rebooted.
If the changes need to be noted (made with the help of this tweak), you should write the following in a notepad:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00
"DisableHWAcceleration"=-
We also save the document under any name, only with the .reg extension.
If you do not want to use registry tweaks, you can manually edit the necessary parameters. To do this, do the following:
- Press "Win + R" and enter "regedit".

- The Registry Editor will open. Go to the branch "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Avalon.Graphics". Here we find the parameter "DisableHWAcceleration". To enable hardware acceleration, set this parameter to 00000001(1). To disable acceleration, change "1" to "0" to get 00000001(0).

- Save the changes and restart the PC.
Thus, by following the steps above, you can enable or disable hardware acceleration in Windows 10.
After turning on the computer for the first time, users notice that not all of the installed RAM in Windows 10 is available. In the characteristics, you can see the value of available much less than the installed RAM. If you start monitoring resources, you can see that more memory is reserved by hardware.
This article will show you how to remove hardware reserved memory in Windows 10. Reserved memory is used by the BIOS or installed device drivers. For example, on laptops it is often found that part of the RAM is given to the integrated video card. But there may be more reasons for hardware reservation of RAM.
Hardware Reserved is RAM that is reserved for use by the BIOS and drivers for other peripherals. If, when viewing the characteristics of the computer, the value of available memory is less than the installed one, then it may have been reserved by the system. The value of reserved memory can be viewed in resource monitoring.
If the value of hardware reserved memory in resource monitoring is very large, then it will be possible to correct the situation. In fact, there can be several reasons for the inaccessibility of all RAM:
- OS bit depth- different bit versions support different amounts of RAM. If the 32-bit version of the system often sees only 3 GB, then the 64-bit version supports 4 GB and more. . If necessary, we recommend switching to the 64-bit version of the system, if you have not already done so.
- Module errors- very often users have to deal with RAM errors, especially if different modules are used. We recommend not only, but also try to start the system with fewer slats. You may be able to find the problem memory module.
- Memory reservation- in this case, a large amount of memory becomes inaccessible, because it falls into the memory reserved by hardware. In principle, resource monitoring easily detects such a problem. Some system configuration changes allow you to remove reserved memory.
- BIOS settings- incorrect settings can also lead to unavailability of RAM in the operating system. Which is actually more common on older laptops. There can be several solutions, ranging from updating the interface, self-configuring settings, and inclusively up to resetting the BIOS settings.
Maximum RAM
We mentioned the system configuration in more detail earlier in the instructions:. In which, in fact, they described many additional parameters. But pay attention to the fact that it is not recommended to make changes to the system configuration yourself, especially if you do not know what a certain parameter means.

The maximum memory setting reduces the performance of your computer. It limits the maximum amount of RAM that a user can use at the system level. It is not recommended to simply change any of the maximum memory values or number of processors.
Checking the BIOS setup options
- Memory remapping function- some motherboards support memory remapping. Memory reallocation gives you access to more memory in Windows 10. The exact name of the memory allocation function varies by manufacturer (in some BIOS versions, you need to look for memory reallocation or extension memory.
- Integrated graphics video aperture size- see how much memory is allocated for the integrated graphics core. This is the amount of memory that the system shares with the video adapter used for texture mapping and rendering. The following default values are available Standard values: 32 Mb, 64 Mb, 128 Mb And Auto.
Some sources and users on the forums advise disabling integrated graphics. If you do not know the main differences between discrete and integrated graphics, we strongly do not recommend disabling it. Additionally, you can try to completely reset the BIOS settings to default.
Conclusion
For some users, it turns out to remove hardware-reserved RAM by removing literally one check mark in Windows 10. But since there can be many reasons, sometimes you have to fiddle with BIOS settings. It can be much easier to restore the BIOS to default values than to look for a specific setting.
The maximum amount of RAM that 32-bit versions of Windows can "see" is 4 GB. Thus, if you have more RAM, you should install the 64-bit version to take advantage of that memory. To find out what version of Windows is installed on your computer, open the "System" item in the control panel (or right-click on "My Computer" and select "Properties").
In the "System type" item, information about the bitness of your version of Windows will be displayed. However, not only the bitness of the system can affect the amount of available RAM in Windows.
Your version of Windows has a maximum memory limit
In addition to the bitness of the operating system, the amount of visible memory is also affected by which edition of Windows you are using. For example, if your computer is running Windows 7 Home, then the maximum available RAM is 2GB, not 4. Users of Windows 7 Home Basic have only 8GB of RAM available, even if they are running a 64-bit version of the OS . There are similar limits for the latest version - Windows 8.
| Version | X86 | X64 |
| Windows 8 Enterprise | 4 GB | 512GB |
| Windows 8 Professional | 4 GB | 512GB |
| Windows 8 | 4 GB | 128GB |
Maximum available RAM in Windows 8
| Version | X86 | X64 |
| Windows 7 Ultimate | 4 GB | 192GB |
| Windows 7 Enterprise | 4 GB | 192GB |
| Windows 7 Professional | 4 GB | 192GB |
| Windows 7 Home Premium | 4 GB | 16 GB |
| Windows 7 Home Basic | 4 GB | 8GB |
| Windows 7 Starter | 2GB | Not available |
Memory is allocated for the operation of the integrated video card or other equipment
Various computer hardware can use some of the system RAM for their work. The most common option is the use of RAM by integrated video controllers (integrated video card). But this is not the only option when the hardware uses RAM.
You can see the amount of RAM used by the built-in video card and other computer hardware in the same System window. If memory is allocated to them, then you will see two values - installed RAM and available for use, which will be displayed in brackets. Accordingly, the difference between them is the size of the RAM that the devices took for themselves.
The motherboard has a limit on the amount of memory
Motherboards also have limits on available RAM. Just because all the memory modules fit into the slots doesn't mean that the motherboard is capable of handling all that memory.
In order to find out if the motherboard sees the memory, enter the BIOS of the computer. To do this, immediately after turning on the PC and before the operating system starts loading, press the appropriate button for this, information about it is usually on the screen (Usually, this is F2 or Delete). In most BIOS versions, you will see information about the installed memory already on the first screen.
If all the memory is visible in the BIOS, but not in Windows, then we are looking for a problem in Windows. If the memory is not displayed in the BIOS, then you should look for a problem at a lower level than the operating system. To get started, you should familiarize yourself with the specifications of the motherboard (for example, find it on the Internet).
Incorrectly installed memory
If you are sure that the motherboard supports the entire amount of installed memory, but it still does not appear in the BIOS, it makes sense to check if you inserted it correctly.
Turn off the power of the computer, open it, it is better if it is grounded. Remove the memory sticks and put them back in carefully, making sure the memory is seated correctly. You can also clean the RAM contacts using a hard eraser.
In some cases, for proper operation of RAM, you need to install it in specific slots - in this case, look for information in the instructions for the computer motherboard.
Another way to diagnose a problem memory module is to remove them one at a time, then turn on the computer and look at the amount of available memory.
Problems with the RAM itself
If you're having any memory issues, it might be the cause itself. You can use a RAM testing utility such as memtest86 or you can use Windows' built-in memory diagnostic utility. You can also recommend testing the memory sticks one by one by installing them into the computer - this way you can more accurately determine the failed module.
I hope this article on the possible reasons why the computer does not see the memory will help you solve the problem.