On new PCs and laptops, you can often find an inefficient allocation of disk space: on the entire hard disk, even if it is a 500- or 1000-gigabyte HDD, not counting small technical partitions, there is only one system C from the partitions of workers. Computer hardware suppliers are not always when installing Windows, they divide the disk into several partitions (C, D, E, etc.), providing the user with the ability to store personal files in safe places protected from Windows crashes. However, the number of partitions on a disk and their size is the sphere of user needs, therefore, the latter should bother with the allocation of disk space. Below we will look at how to divide a hard drive consisting of one C partition with Windows installed on it into several partitions using AOMEI Partition Assistant. We will use its Standard Edition, which is distributed free of charge.
AOMEI Partition Assistant is a rare occasion when a professional-grade functional program comes free of charge. The expansion of its capabilities is provided for in paid editions, but even in the free edition we will find everything you need to organize disk space, and not only at the basic level, but also at the advanced level. If we are talking only about dividing a disk into partitions, this can be done without resorting to third-party software, using the standard utility of the Disk Management system. But AOMEI Partition Assistant has more potential: mastering it will take the user to a new, higher level of computer skills and allow him to solve many disk problems on his own. So, even such a seemingly simple operation as partitioning a disk into partitions, the AOMEI Partition Assistant program will allow you to carry out in various ways - by dividing the partition and by changing its size. We will consider all this in detail below, but first a couple of words directly about the size of section C.
Before proceeding with the division of section C, it is necessary to decide on the size left to it. In order to prevent data loss and Windows disruption, AOMEI Partition Assistant will not allow you to shrink the C partition to a size smaller than the actual size of the data. But the size of partition C should not be equal to its actually occupied space. For Windows to work properly, it is necessary that about 20% of the volume of the C partition remain free. It is desirable that the C partition be at least 80 GB, and better - 100 GB. The data is given without taking into account the installation of certain resource-intensive games and programs on the system partition.
1. Splitting a section
Partitioning is the creation of non-system partitions by dividing existing partitions into two parts. First, section C is divided into two parts, then section D is divided into two in the same way, and so on. This method is a couple of steps simpler than its alternative - the operation to resize the original partition, which will be discussed below. Partitions formed as a result of division automatically receive their letter and "inherit" the file system from the original partition, and on MBR disks, the type is also primary (main). Only the fourth section will be automatically created with a boolean type.
In the AOMEI Partition Assistant window, click on partition C and click on the "Partition partition" context menu option.
Moving the slider of the graphic block, we form the sizes of the sections. For section C we leave, for example, 80-100 GB, and give everything else to section D. Next, click the "Advanced" button at the bottom and activate the option. Click "Ok".

In the main window of the program, we will see a picture of the partitions, which it is not yet, but will be after the application of the planned operations. AOMEI Partition Assistant provides for carrying out several designated operations in a single process. So, in the way described above, the newly formed section D can be divided into two more sections - one smaller, one larger. And the larger section, in turn, can be divided into two more parts. Etc.
After completing the formation of the sections, we can add some more operations. The section context menu, the functions of which are duplicated on the operation panel on the left of the window, allows you to assign the necessary letters to the formed sections and give them your own names (change labels).
 3
3 If you need to install for some of the partitions of the file system, not NTFS, but another, formatting with a change of the file system can be added to the already planned operations.
 4
4 Once everything is ready, you can start applying the scheduled operations. To do this, press the "Apply" button.
 5
5 Then we confirm the decision twice - in the list of pending operations and in the window warning about the need to perform operations in the pre-boot mode of the system.

We are waiting for the completion of the work of AOMEI Partition Assistant and after rebooting the system we check the results.
2. Resize the partition
Partition resizing is a way of creating non-system partitions in which the size of the C partition is reduced, while the freed space remains unallocated. From it, respectively, you can form sections. The advantage of this method is to set the desired parameters of the partitions immediately upon their creation. In the AOMEI Partition Assistant window, click on partition C and click "Resize Partition".
 7
7 Move the slider of the graphic box to the left until the C section is reduced to the desired size. Next, click "Advanced" and set the option to align partitions. Click "Ok".

Returning to the main window of the program, click the unallocated space formed as a result of the previous operation and click "Create a section".
 9
9 A special form will appear, where for the future section we can immediately select a letter and a file system. If not all disk space is allocated for the partition, we reduce it by moving the slider of the graphic block to the left. Next, click the "Advanced" button.

In the extended mode of this form on MBR disks, we can select the type of partition - primary or logical. Having decided on the settings, we check that the option to align partitions is active, and then click "OK".

We apply the planned operations and confirm them.
 12
12 
Have a great day!
Why is it necessary to share a hard drive in Windows? Primarily for the safety of your personal data. When a hard disk has only one partition, then all the files that are on this disk: programs, documents, photos, files of the Windows operating system itself are stored in one place.
Now imagine that the system is crashing. All your personal files (photos, documents) are likely to be lost. It is much more correct when system files and user files are stored separately from each other.
Physically, they will still remain on the same hard drive, but they will be on different partitions. There can be several sections. One, as a rule, is reserved for the operating system and programs (system partition), the other (or others) for user files.
One of the easiest and most affordable ways is to partition the hard drive when installing Windows. How to do this, we have analyzed in great detail and with a specific example in. What if the system is already installed and there are user files in it, how to partition the disk in such cases?
How to partition a disk with Windows installed without losing data
Today we will analyze how to divide a hard drive into two or more partitions with an OS already installed. Moreover, it does not matter at all which edition of Windows you are using. This method will be relevant for any version, be it Windows 7 or Windows 10. In addition, if you already have two partitions, but you need to create a third, both methods described below will also work.
In fact, our task is to "pinch off" a large partition (and in our case this is the only partition - the system drive C) some part, say 200 GB, and make a separate partition out of it.
This can be done in several ways, including using the Windows operating system itself, which has a special Disk Management tool. This method requires a minimum of effort and in most cases solves the task without third-party software. Let's start with him.
Before you start partitioning your Windows hard drive, you need to take some precautions. If there are important files in the system, copy them to an external medium (USB flash drive, external hard drive) in advance.
How do I split my hard drive into two or more partitions? Method 1 - by means of Windows system
Let's use the Disk Management tool. In Windows 10, just right-click on the icon My computer, select item Control - Disk management.
In other versions of Windows, this tool can be found using the regular search or using the hotkey combination Win + R, and enter the command diskmgmt.msc.

Before us is the Disk Management window, where the user's disk is displayed, which in this case has a size of 465.76 GB (Disk 0). Almost all the HDD space is allocated to one section - Disk C. There is also a section (500 MB), which is reserved by the operating system at the stage of its installation.

In our case, 465 GB (the entire hard disk) for one system disk is not a permissible luxury, so we will "pinch off" the maximum possible (as the system will allow) number of GB and make a new partition out of this free space.
As a rule, about 100-150 GB are allocated for the system disk. It all depends on the specific user. 100 GB is quite enough if Windows and the most necessary software are installed on the system disk. If, in addition to the system and software, it is planned to install modern games, then the size of 100 GB will clearly not be enough.
Before performing any operation on a specific hard disk partition, do not forget to select it. It is enough to click on it with the left mouse button and the section will be selected. Only then proceed with the operation.
Let's move on to practice. Select the section from which you want to "pinch off" the space. On the selected section, right-click and select the command Shrink volume.

All sizes are in megabytes, be careful. In a specific example, the maximum number of MB that the system "allows" to compress is 237.656 MB (232.09 GB). This means that after compression, we get a 232 GB Disk C and a D Disk 238782 MB (233 GB). Not the best option. If it does not suit you, and you need to "pinch off" more than the system offers, then you will have to use third-party software, but more on that later.

When all calculations are completed, and the sizes of future sections are set, click OK(or click Enter). We have a new unrecognized partition (200 GB). Take your time to exit Disk Management. The process of dividing the disk into two partitions is not over yet. Select a new section (200 GB), and right-click, select the item Create simple volume.

Run Simple Volume Wizard... In principle, everything is simple further, it is enough just to follow the instructions of the master himself. Check out the screenshots. You are required to give the future partition a letter (in my case, it is D) and the file system - NFTS.




Let's see what happened. We have one hard drive and have divided it into two partitions: the system Drive C (265 GB) and the New volume D (200 GB) for storing personal data. By the way, the new volume is now displayed in Windows Explorer as well.

Now you know how to partition a hard drive into two or more partitions using Windows. If this method suits you, and it coped with your task, then you can stop at this. However, if you are looking for a better option, and, for example, you need to “pinch off” a larger size than the system itself offers, we use third-party software. However, first we need to restore the original state of the hard drive.
Let's delete the created partition and return it to the system disk. Highlight New volume and right-click on the item Delete volume.

We read the warning and click OK... We get 200 GB that are not allocated.


We carefully check all the numbers and click Further.

We returned to the initial state when the system has one hard disk and it is almost completely allocated for one partition (system).
How do I split my hard drive into two or more partitions? Method 2 - Partition Master Free
It's time to move on to third-party software. There is a great choice here. There are paid and free options. I recommend staying at. Why? Time-tested, intuitive interface, free. Unlike the Disk Management tool that Windows offers, Partition Master allows you to shrink a disk partition as long as it is physically possible.

The official website of the program is www.partition-tool.com. Go to the site, and select the Products - Partition Master Free section in the top menu - Download.
Since the program is free, during its installation you will be prompted to install additional unwanted programs. Many free products work great and do their job perfectly, but since they are free, developers are trying to make some money on them. Be careful and uncheck the checkboxes with the offer of promotional products in time.
1. Launch the installation of the downloaded program. Choose the language English and press OK.
2. In the next window, we agree that we will use this software only for our family, put a tick and click OK.
3. In the next window (at your discretion) we leave only one checkbox - Create a desktop icon(create an icon on the desktop) and click NEXT.
Installing Partition Master Free in screenshots. Click




5. In the next window, enter your Name and Email... You can enter fictitious data.
6. After installation, click Finish.
The program should start. The interface is completely in English, but it is quite simple and with the help of this instruction it will not be difficult to partition a disk in Partition Master Free.
The main window of the program displays Drive C, which you want to split. Here, its basic information is presented: file system (NFTS), size - actual (465.27 GB) and used (17.10 GB). Pay attention to the graphical disc scale, which is located at the bottom of the window. You can work and execute commands using both options. With a graphical scale, this is a little easier and clearer.

Select the section (left-click) that you want to split (from which you need to pinch off the space), and select the (Resize) item in the drop-down list of commands.

In the window that appears, grab and move a special slider. He is responsible for the set size of the future partition. We indicate how many GB we need to pinch off. In this case, 322.242 MB (or 314.69 GB) is selected for the new partition.
Pay attention to the bottom of the window. As you move the slider, you can see in real time how your C Drive will change after compression, and how much will be allocated for the new partition.
I have set the size of the new partition to 314 GB, and the size of the C drive will become 150 GB. After that we press OK.

An unrecognized partition (314 GB) has appeared. Now we need to make a section out of this unrecognized space.
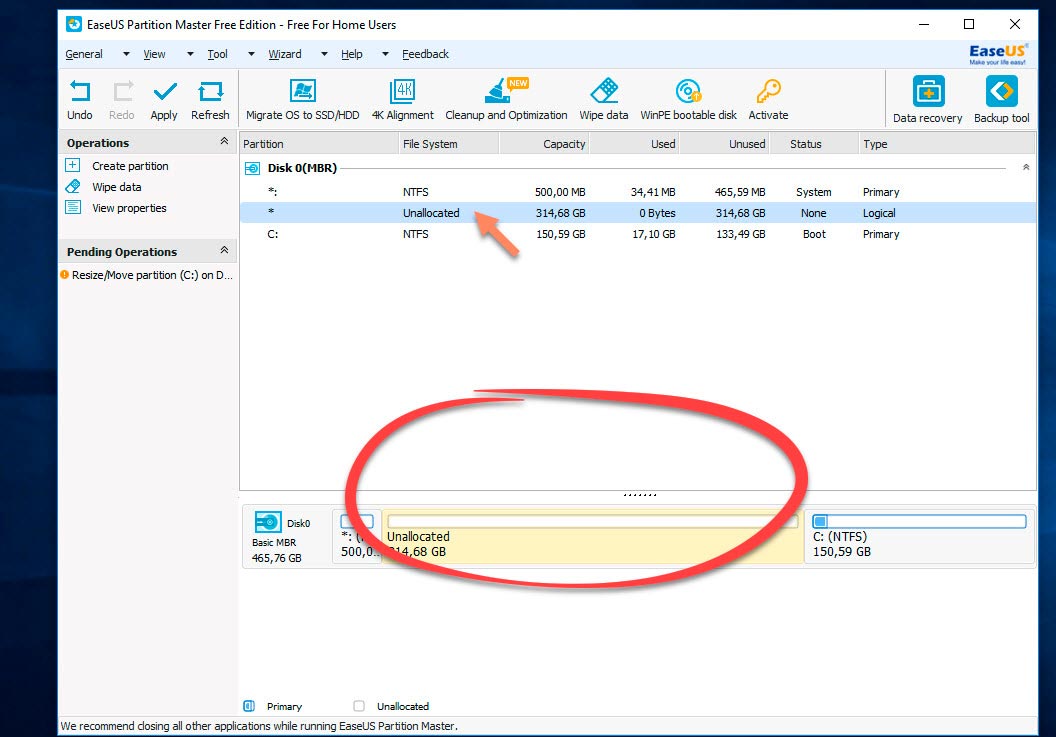
Click on it with the mouse and select the command (Create section) in the drop-down menu.

In a new window, I am asked to enter a partition label, give it a name (Partition Label). Let's say I call it Multimedia. Next, you need to specify the letter of the section (Drive Letter). Do not forget about the point Optimizefor SSD, but only if you have an SSD drive. If you are using a regular hard disk, then this item is not checked. The file system (File Systems) - NFTS. Click OK.

Let's see what happened. System Disk C for which we allocated approximately 150 GB and a partition for storing files (Multimedia). This is not the final result, but a kind of sketch. For the program to perform all operations, you need to click on the button Apply in the top menu.

A pop-up window will appear in which information about the operations that will now be performed will be indicated. Push YES and the program will start executing them. The computer will restart and start in boot mode. Wait for the end of the operation.

After the end of the process, a window will appear with information that the two operations have been successfully completed. If you open the explorer, you can see the created new section.

System files and user files will now be kept separate. The task has been completed. As you can see, both of the described methods are working and allow you to partition the disk without losing data. Which one to choose - everyone decides for himself. I hope this article was useful and helped you finally understand this issue.
If you are assembling a computer and are looking for the best prices for components, then the number one option is computeruniverse.ru. A proven German store. Coupon for 5% euro discount - FWXENXI... Happy build!
Tweet
The hard drive on your computer and the disk icon in My Computer are different concepts. For example, a computer might have one hard drive, while My Computer might have several. The reason for this strange inconsistency is that the hard drive can be divided into so-called partitions. This is called logical disk layout.
I will talk about why such markup is needed, how to do it correctly (and whether it should be done at all), and also talk about free programs for such a delicate procedure.
Why you need to divide your hard drive into partitions
There are several reasons for dividing a hard disk into partitions:
- Partitions on a hard disk are primarily needed for competent storage of information. For example, some users prefer the following division: the operating system and programs on the same disk (usually C), documents - on the second ( D), archive of photos on the third ( E) etc. In this case, the hard drive may well be one.
- If you have one hard drive, but you want to have two or more operating systems, you will have to divide the hard drive into partitions, since Windows and other operating systems can only be installed on different partitions or hard drives.
- Laptop manufacturers (and some computers from well-known manufacturers, such as Acer) have their own reason to divide hard disk partitions: on a partition that is visible as a disk C, Windows is installed, the second ( D) is absolutely empty, and the third one (which is not visible in any way in the "My Computer" window) stores a compressed copy of the partition C... This hidden hard disk partition is called recovery partition... If something happened to the operating system ("Windows flew" - as some users like to say), then when you turn on the laptop, just press the key combination (which one - see the instructions for the laptop) and a special program will clear the disk C, then unpacks the contents of the hidden section there. As a result, the user will receive a laptop with the programs that were originally on it at the time of purchase in the store. Disk D it will not be changed. The conclusion suggests itself: if all documents are stored on a laptop with such a recovery system not on drive C, a only on D, it will be possible at any time to restore damaged Windows with a brand new one, without losing important data for yourself. By the way, any advanced user can make such a recovery system for himself, but I'll tell you about it some other time.
- Operating systems Windows 7 and Windows 8, when installed on a clean, "unpartitioned" hard drive, create a hidden partition with a size of 100-350 megabytes. This small section contains the bootloader, which is, oddly enough, to boot Windows. This section will not be or its contents will be damaged - and the computer will not start the operating system, displaying an inscription on a black screen "Boot fail", "Cannot find boot device", "Boot error" or similar, the meaning of which is the same - the boot disk with operating system. Actually, the bootloader can be stored on disk. C:, and / or in hidden sectors of the hard disk (outside partitions), but the developers decided to use a separate hidden partition in Windows 7/8 in order to somehow protect the bootloader from being damaged by other programs, viruses or the user.
- There are other reasons for partitioning a hard drive. For example, for the correct operation of GNU / Linux operating systems, several partitions should be created, but this is a topic for a separate article, we will not consider them here.
So, The main reasons for partitioning a hard drive are: for the convenience of storing information, for installing several operating systems, for the recovery system, for storing the Windows 7/8 boot loader.
A bit of theory: file systems, partition types
Information about partitions (ie logical disks) is stored in a "partition table". Each logical drive can have its own file system. You can read more about all this in the Wikipedia articles: Disk Partition, Logical Disk, File System. For a beginner, it is enough to know the very minimum:
- If you divide the hard disk into logical disks (partitions), disk capacity will not increase- there is simply nowhere to free space! You can make partitions of any size, but in total they cannot be larger than the size of a real hard disk. Here is less - please. Then you get unallocated free space not visible in My Computer, from which you can get one or more new partitions. This is a question I often get from newbies, so I put it first.
- Exists primary (main) and extended (additional) sections. One hard disk cannot have more than four main partitions (why so - see the links above), so they came up with an extended partition - this is a primary partition that can include as many partitions as you want. As a result, thanks to the extended partition, a hard disk can have as many partitions as you like - dozens, hundreds.
- Each partition can have its own file system. Currently, only NTFS can be used to install Windows Vista, 7 and 8, and the outdated Windows XP can be installed on disks with the FAT32 file system. However, I do not recommend doing this, as it imposes too many restrictions. Make all partitions in NTFS - everything will work as it should.
- Any hard drive must be partitioned one way or another. Into one or more logical drives - it's up to you. When buying a hard drive, it is usually already divided into one section - so the manufacturer decided. If you are satisfied with this way of organizing information, do not touch it.
- It is very undesirable to do disk partitioning in laptops - most of them have hidden recovery partitions that can be damaged (see point 3 of the previous chapter).
- If you bought a 2 terabyte hard drive, and My Computer has “only” 1.86 terabytes (1,860 gigabytes), then don't rush back to the store. It's all about how the manufacturers and Windows consider the volume. Read more about this in the Wikipedia Hard Drive article. The larger the size of the hard disk, the more clearly you can see that the real gigabytes are smaller.
- Sections can delete, create, shift(change their physical position on the disk), resize, format, convert file systems on partitions from one to another. Moreover, many programs are able to do this while preserving all data. There are other operations, but novice users most often need the above.
- In the event of an error in the process of changing sections (see paragraph 7), information is almost always lost. Yes, it will be possible to restore it (or part of it) using special programs with the participation of specialists, but it is best to save all important information on other disks (not logical, but real disks) or flash drives in advance, so as not to pay money for data recovery.
Disk Management snap-in for Windows
Windows has a standard tool for changing partitions - " Disk management". Depending on the version of Windows, the capabilities of this program change slightly, but in general over the past years (if we talk about Windows Vista, 7, 8) there have been no major changes. Windows XP looks more modest in this regard - apart from formatting and changing the drive letter, there is little you can do.
As an example I will take “ Disk management»Windows 7. You can open this program in several ways:
- The simplest - right-click on the line A computer on the menu Start- select the item Control- in the new window select Disk management.
- We open Control Panel - Administration - Computer management - Disk management.
- Push Start - Execute(or the keyboard shortcut Win + R) - enter in the window that opens diskmgmt.msc- press OK.
Disk management looks like that:
Here you can see both physical disks (including DVD drives, flash drives and other devices for storing information), and logical ones, i.e. virtual - hidden partition of the bootloader Windows 7, disks C and D... The number of disks on your computer may be different.
The main actions are available by right-clicking on the desired section:
The list of actions is rather meager:
- Items Open, Conductor allow you to see the contents of the disks
- Make a section active- indicate on which disk (partition) the loader is located. In Windows 7 and 8, this is a system-reserved partition. You cannot make another partition active - the operating system will stop loading.
- Change drive letter or drive path- you can change the drive letter displayed in the "Computer" window or display it as a folder. Yes, partitions can be displayed not only as disks, but also as folders on any disk.
- Format- you can read about it in the article Formatting Wikipedia. The item opens a window with which you can start high-level formatting.
- Expand volume- if there is space on the hard disk that is not marked as a partition, then you can expand the size of the partition at the expense of this free space.
- Shrink volume- this item allows you to reduce the size of the partition. The result will be the formation of unallocated space, which can be put into action - to expand the volume of another section (see the previous paragraph).
- Delete volume- delete a section. Don't click on an item without carefully considering the consequences. If you delete a section, then the information on it will be possible to save only with the help of special programs, and even then not always.
- Properties- a properties window will open with information about the selected disk (partition).
Of course, this is not a complete list of possibilities. Disk management... You can create dynamic disks, for example. However, novice users do not need this, this article is designed just for them.
So, to create, delete, resize partitions via Disk management, only three menu items are needed: Expand volume, Shrink volume, Delete volume.
All operations take place in real time, i.e. after clicking the desired item and an affirmative answer to the question - do we want to do this - the actual action takes place.
Do not forget that there is a risk of failure, due to which we can lose both one section and all. This applies primarily to computers with a large number of unnecessary programs - each of them may be the culprit for the deletion of all data. Moreover, the scenario when you need to change the partition from which Windows is started (usually this is a disk C), is the worst - most often users experience problems when they try to change the system partition.
To minimize the risk of failure, there are three methods:
- Insert the hard drive into another computer and change partitions from it by running Disk management or any other program for changing partitions. Due to the fact that Windows will be started from a different disk, no programs will climb onto the other disk, interfering with the critical operation.
- Boot from Live CD - the operating system and programs will be launched not from the hard drive, but from CD or DVD, flash drives - again, nothing will interfere with changing partitions.
- Use a program that can work in Native mode to change sections. For example, checking the disk C always works in this mode - black window with white text before loading the desktop. In this mode, a minimum of programs are running, the risk of failure is minimal.
The third option is the simplest, because the user doesn't really need to do anything - just restart the computer and wait a few minutes. The following two survey programs are able to do this.
Free for home use program for changing hard disk partitions.
By clicking on the section (it doesn't matter - in the list above, in the picture below), you can see the menu (both pop-up and on the left panel) with all the requested actions:
Resize / Move partition- resize the partition and / or shift its physical position on the disk. By the way, the official website says that the EaseUS Partition Master Home (free) version does not support changing partitions. It is not - everything works great.
Copy partition- copy the partition to another disk with all the information available on it.
Merge partitions- merging two or more sections. Convenient if you need to save information on your hard disk, but reduce the number of partitions. Convert to logical / primary- conversion to logical (extended) / main (primary) partition.
Change label- change the disc label.
Change drive letter- change the drive letter.
Defragment- launching the standard Windows program for disk defragmentation.
Check partition- Checking the disk for errors using, again, the standard Windows program.
Hide partition- make sure that the section is not visible in the "Computer" window.
Delete partition- deleting a section.
Format partition- section formatting.
Wipe partition- clearing the contents of the section. All folders and files will be deleted, the section will remain. Information deleted in this way cannot be recovered.
Explore partition- view the contents of the section.
View properties- see how much space is occupied on the partition, what file system it has and find out other technical information.
The list of actions changes depending on where you click. In the screenshot above, I clicked on the non-system partition. By clicking on the system partition (from where Windows is running), there will be no items for deleting, hiding, cleaning. If you click on the physical disk icon, the list of actions will be completely different:
I will list the points:
Copy disk- the contents of the entire disk are copied: sections, information in them. This requires a second disk of the same or larger capacity.
Upgrade disk- the function is primarily needed to transfer Windows to a new larger hard drive. The partition is copied and enlarged in proportion to the size of the new hard disk.
Delete all partitions- delete all sections.
Wipe disk- the same as the previous point, only with special deletion algorithms, due to which the information will be impossible to recover.
Surface test- Checking the surface of the disk (physical). Allows you to detect bad sectors (the so-called "bad", "bad blocks").
View properties- display information about the disc.
Yes, knowledge of English is clearly required here, especially when you consider that almost every item calls up a window with settings for the action to be performed. After you make the necessary manipulations, you need to apply the changes by clicking the button Apply(Apply):
Only then will the partition change begin. This process can take some time - from a couple of minutes to several hours.
Depending on whether the system partition is affected or not, the operations are carried out either immediately in the window, or you will need to restart the computer and start changing the partition in Native mode:
The program has a lot of functions, it's hard to list them all. I recommend that you read the help for EaseUS Partition Master. It is in English, unfortunately, but you can use the Google translator. The translation is quite understandable.
Pros of EaseUS Partition Master Home Edition:
- There are a lot of functions.
- All actions are "virtual" until the Apply button is pressed. So, you can undo operations before this "point of no return" and try to do something else with the partitions. Or not at all if you change your mind.
- Works consistently and predictably. For example, during testing while changing partitions, I started copying files to the partition to be changed. Bottom line - a window appeared stating that the partition could not be locked, all operations were interrupted, the data did not disappear anywhere.
- The program is free for home use.
Cons of EaseUS Partition Master Home Edition:
- The interface is in English only.
- There are probably too many opportunities - this can confuse beginners.
- A serious failure during the operation will lead to serious consequences.
- For example, if you turn off the computer while changing the partition, the data on the partition will disappear. However, this is a minus of absolutely all programs for changing partitions.
Output: the program is good. You can and should use it, there is no alternative among free programs.
Paragon Partition Manager 11 Free
Free program for changing partitions from a company based in Russia. Unfortunately, the program is in English. What made the developers take such a step is not clear. Moreover, the paid version of the program is Russian.
The main window of the program is no different from the hero window of the previous review, except that the buttons have changed their order:
Deserves special mention Express Mode(Simplified mode). By clicking on this button, we will get a window with a list of the most frequent actions:
One could say that this is an ideal mode for beginners, if not for one "but": everything here is in English. Moreover, I had a suspicion that the English here was somehow wrong, as if it was not a person who translated, but a machine.
Pros of Paragon Partition Manager 11 Free:
- Many windows are clear enough to understand the functions.
- Some operations are carried out directly in the program window, some (if required) in Native mode. That is, the program does everything to reduce the chance of data loss.
- The program is free to use at home.
Cons of Paragon Partition Manager 11 Free:
- English-speaking, and because of the strange construction of phrases, it is quite difficult to perceive.
- The simplified Express Mode works exactly the opposite: first, the descriptions of operations and the operations themselves have more technical subtleties than required; secondly, this mode is very capricious and does not really work, giving out meaningless errors.
- The program is running too slowly. For example, it took me about 5 minutes to delete a 38GB hard drive partition - long enough for such a simple operation.
Output: the program works, but somehow unpredictable. I do not recommend using this program, since there is an alternative in the form of EaseUS Partition Master Home.
Changing partitions during installation of Windows 7, 8, 10
This tool deserves a mention too.
We take any installation disk with Windows Vista, Windows 7, 8 or 10, start the installation of the disk, go to the partition selection and click Disk setup:
Everything seems to be simple: you need to click on a section in the list, then the action button. Unfortunately, there is little action here: deletion, formatting, partition creation and expansion.
You can, for example, delete a partition and, at the expense of the free space, increase the size of another partition or partitions (selecting the desired partitions, press the Delete and Expand buttons one by one).
Alas, a very popular operation - reducing the size of partitions - is not here. You can delete a partition, then re-create a new one with a smaller partition, but, unfortunately, we will lose data in this case.
All operations take place in real time, i.e. after pressing the button, the action takes place.
Outcome: editing partitions during Windows setup is a very primitive tool. Works, but performs only a limited list of actions, among which the only one that saves data is increasing (expanding) the size of the partition. If you need to install Windows and do not need to save data on partitions, then the tool will come in handy.
If suddenly you accidentally deleted a partition during Windows installation or through any program, do not despair - the partition recovery function is available in EaseUS Partition Master Home Edition.
In order to recover a deleted hard disk partition, do not touch sections, immediately boot into Windows (or insert the hard drive into another computer if you deleted the system partition and Windows cannot boot), then run the above program, click on the line with the word in the list Unallocated("Unassigned"), then click Partition recovery.
The rest, as they say, is a matter of technology - the action wizard will tell you where to click, where to tick, then restore your deleted disk.
Tip # 2: Install two or more Windows operating systems on one hard drive
All it takes is several sections. If the hard disk already has a second partition, which is visible in the window " A computer"- make sure that there is at least 20 GB of free space (more is better), then during Windows installation, simply specify this second (third, fourth, etc.) drive. Once installed, you will be able to select Windows using the menu that appears when you turn on your computer.
If you have one disk ( C), I suggest the simplest option: Through Disk management first give the section WITH command Shrink, having reduced by at least 20 gigabytes (or better - more, because in addition to Windows, you will also install programs):
Right-click on the C drive ...
After pressing the button Shrink disk size C decreases, unallocated (free) space appears in the partition map:

We indicate unallocated space. The section will be created by the installer itself.
After installation, you will have two operating systems. You can make more unallocated spaces or empty disks, specify them for installation.
Thanks to reader Vladimir for bringing up this topic.
You may have noticed that in the screenshots of the Disk Management window, all partitions are marked with a blue stripe. You may have sections with green stripes. What is the difference between the blue and green sections?
A green bar in Disk Management is a sign of an extended (additional) partition. As I already wrote above, inside there may be "nested" sections, which from the user's point of view are no different from the main (primary) sections. Nested partitions have one peculiarity - if you reduce their size, then due to the free space that appears, it will not be possible to expand the main partition just like that. You must first compress the extended partition itself (which stores free space and a smaller partition) in order to create free space outside any partitions, only then you can expand the disks.
Standard Disk Management does not know how to work normally with extended disks, so if you see green marks instead of blue ones, it is better to use the free programs above - they will reduce extended partitions, move free space where necessary and expand the main disk.
Tweet
The hard drive on your computer and the disk icon in My Computer are different concepts. For example, a computer might have one hard drive, while My Computer might have several. The reason for this strange inconsistency is that the hard drive can be divided into so-called partitions. This is called logical disk layout.
I will talk about why such markup is needed, how to do it correctly (and whether it should be done at all), and also talk about free programs for such a delicate procedure.
Why you need to divide your hard drive into partitions
There are several reasons for dividing a hard disk into partitions:
- Partitions on a hard disk are primarily needed for competent storage of information. For example, some users prefer the following division: the operating system and programs on the same disk (usually C), documents - on the second ( D), archive of photos on the third ( E) etc. In this case, the hard drive may well be one.
- If you have one hard drive, but you want to have two or more operating systems, you will have to divide the hard drive into partitions, since Windows and other operating systems can only be installed on different partitions or hard drives.
- Laptop manufacturers (and some computers from well-known manufacturers, such as Acer) have their own reason to divide hard disk partitions: on a partition that is visible as a disk C, Windows is installed, the second ( D) is absolutely empty, and the third one (which is not visible in any way in the "My Computer" window) stores a compressed copy of the partition C... This hidden hard disk partition is called recovery partition... If something happened to the operating system ("Windows flew" - as some users like to say), then when you turn on the laptop, just press the key combination (which one - see the instructions for the laptop) and a special program will clear the disk C, then unpacks the contents of the hidden section there. As a result, the user will receive a laptop with the programs that were originally on it at the time of purchase in the store. Disk D it will not be changed. The conclusion suggests itself: if all documents are stored on a laptop with such a recovery system not on drive C, a only on D, it will be possible at any time to restore damaged Windows with a brand new one, without losing important data for yourself. By the way, any advanced user can make such a recovery system for himself, but I'll tell you about it some other time.
- Operating systems Windows 7 and Windows 8, when installed on a clean, "unpartitioned" hard drive, create a hidden partition with a size of 100-350 megabytes. This small section contains the bootloader, which is, oddly enough, to boot Windows. This section will not be or its contents will be damaged - and the computer will not start the operating system, displaying an inscription on a black screen "Boot fail", "Cannot find boot device", "Boot error" or similar, the meaning of which is the same - the boot disk with operating system. Actually, the bootloader can be stored on disk. C:, and / or in hidden sectors of the hard disk (outside partitions), but the developers decided to use a separate hidden partition in Windows 7/8 in order to somehow protect the bootloader from being damaged by other programs, viruses or the user.
- There are other reasons for partitioning a hard drive. For example, for the correct operation of GNU / Linux operating systems, several partitions should be created, but this is a topic for a separate article, we will not consider them here.
So, The main reasons for partitioning a hard drive are: for the convenience of storing information, for installing several operating systems, for the recovery system, for storing the Windows 7/8 boot loader.
A bit of theory: file systems, partition types
Information about partitions (ie logical disks) is stored in a "partition table". Each logical drive can have its own file system. You can read more about all this in the Wikipedia articles: Disk Partition, Logical Disk, File System. For a beginner, it is enough to know the very minimum:
- If you divide the hard disk into logical disks (partitions), disk capacity will not increase- there is simply nowhere to free space! You can make partitions of any size, but in total they cannot be larger than the size of a real hard disk. Here is less - please. Then you get unallocated free space not visible in My Computer, from which you can get one or more new partitions. This is a question I often get from newbies, so I put it first.
- Exists primary (main) and extended (additional) sections. One hard disk cannot have more than four main partitions (why so - see the links above), so they came up with an extended partition - this is a primary partition that can include as many partitions as you want. As a result, thanks to the extended partition, a hard disk can have as many partitions as you like - dozens, hundreds.
- Each partition can have its own file system. Currently, only NTFS can be used to install Windows Vista, 7 and 8, and the outdated Windows XP can be installed on disks with the FAT32 file system. However, I do not recommend doing this, as it imposes too many restrictions. Make all partitions in NTFS - everything will work as it should.
- Any hard drive must be partitioned one way or another. Into one or more logical drives - it's up to you. When buying a hard drive, it is usually already divided into one section - so the manufacturer decided. If you are satisfied with this way of organizing information, do not touch it.
- It is very undesirable to do disk partitioning in laptops - most of them have hidden recovery partitions that can be damaged (see point 3 of the previous chapter).
- If you bought a 2 terabyte hard drive, and My Computer has “only” 1.86 terabytes (1,860 gigabytes), then don't rush back to the store. It's all about how the manufacturers and Windows consider the volume. Read more about this in the Wikipedia Hard Drive article. The larger the size of the hard disk, the more clearly you can see that the real gigabytes are smaller.
- Sections can delete, create, shift(change their physical position on the disk), resize, format, convert file systems on partitions from one to another. Moreover, many programs are able to do this while preserving all data. There are other operations, but novice users most often need the above.
- In the event of an error in the process of changing sections (see paragraph 7), information is almost always lost. Yes, it will be possible to restore it (or part of it) using special programs with the participation of specialists, but it is best to save all important information on other disks (not logical, but real disks) or flash drives in advance, so as not to pay money for data recovery.
Disk Management snap-in for Windows
Windows has a standard tool for changing partitions - " Disk management". Depending on the version of Windows, the capabilities of this program change slightly, but in general over the past years (if we talk about Windows Vista, 7, 8) there have been no major changes. Windows XP looks more modest in this regard - apart from formatting and changing the drive letter, there is little you can do.
As an example I will take “ Disk management»Windows 7. You can open this program in several ways:
- The simplest - right-click on the line A computer on the menu Start- select the item Control- in the new window select Disk management.
- We open Control Panel - Administration - Computer management - Disk management.
- Push Start - Execute(or the keyboard shortcut Win + R) - enter in the window that opens diskmgmt.msc- press OK.
Disk management looks like that:
Here you can see both physical disks (including DVD drives, flash drives and other devices for storing information), and logical ones, i.e. virtual - hidden partition of the bootloader Windows 7, disks C and D... The number of disks on your computer may be different.
The main actions are available by right-clicking on the desired section:
The list of actions is rather meager:
- Items Open, Conductor allow you to see the contents of the disks
- Make a section active- indicate on which disk (partition) the loader is located. In Windows 7 and 8, this is a system-reserved partition. You cannot make another partition active - the operating system will stop loading.
- Change drive letter or drive path- you can change the drive letter displayed in the "Computer" window or display it as a folder. Yes, partitions can be displayed not only as disks, but also as folders on any disk.
- Format- you can read about it in the article Formatting Wikipedia. The item opens a window with which you can start high-level formatting.
- Expand volume- if there is space on the hard disk that is not marked as a partition, then you can expand the size of the partition at the expense of this free space.
- Shrink volume- this item allows you to reduce the size of the partition. The result will be the formation of unallocated space, which can be put into action - to expand the volume of another section (see the previous paragraph).
- Delete volume- delete a section. Don't click on an item without carefully considering the consequences. If you delete a section, then the information on it will be possible to save only with the help of special programs, and even then not always.
- Properties- a properties window will open with information about the selected disk (partition).
Of course, this is not a complete list of possibilities. Disk management... You can create dynamic disks, for example. However, novice users do not need this, this article is designed just for them.
So, to create, delete, resize partitions via Disk management, only three menu items are needed: Expand volume, Shrink volume, Delete volume.
All operations take place in real time, i.e. after clicking the desired item and an affirmative answer to the question - do we want to do this - the actual action takes place.
Do not forget that there is a risk of failure, due to which we can lose both one section and all. This applies primarily to computers with a large number of unnecessary programs - each of them may be the culprit for the deletion of all data. Moreover, the scenario when you need to change the partition from which Windows is started (usually this is a disk C), is the worst - most often users experience problems when they try to change the system partition.
To minimize the risk of failure, there are three methods:
- Insert the hard drive into another computer and change partitions from it by running Disk management or any other program for changing partitions. Due to the fact that Windows will be started from a different disk, no programs will climb onto the other disk, interfering with the critical operation.
- Boot from Live CD - the operating system and programs will be launched not from the hard drive, but from CD or DVD, flash drives - again, nothing will interfere with changing partitions.
- Use a program that can work in Native mode to change sections. For example, checking the disk C always works in this mode - black window with white text before loading the desktop. In this mode, a minimum of programs are running, the risk of failure is minimal.
The third option is the simplest, because the user doesn't really need to do anything - just restart the computer and wait a few minutes. The following two survey programs are able to do this.
Free for home use program for changing hard disk partitions.
By clicking on the section (it doesn't matter - in the list above, in the picture below), you can see the menu (both pop-up and on the left panel) with all the requested actions:
Resize / Move partition- resize the partition and / or shift its physical position on the disk. By the way, the official website says that the EaseUS Partition Master Home (free) version does not support changing partitions. It is not - everything works great.
Copy partition- copy the partition to another disk with all the information available on it.
Merge partitions- merging two or more sections. Convenient if you need to save information on your hard disk, but reduce the number of partitions. Convert to logical / primary- conversion to logical (extended) / main (primary) partition.
Change label- change the disc label.
Change drive letter- change the drive letter.
Defragment- launching the standard Windows program for disk defragmentation.
Check partition- Checking the disk for errors using, again, the standard Windows program.
Hide partition- make sure that the section is not visible in the "Computer" window.
Delete partition- deleting a section.
Format partition- section formatting.
Wipe partition- clearing the contents of the section. All folders and files will be deleted, the section will remain. Information deleted in this way cannot be recovered.
Explore partition- view the contents of the section.
View properties- see how much space is occupied on the partition, what file system it has and find out other technical information.
The list of actions changes depending on where you click. In the screenshot above, I clicked on the non-system partition. By clicking on the system partition (from where Windows is running), there will be no items for deleting, hiding, cleaning. If you click on the physical disk icon, the list of actions will be completely different:
I will list the points:
Copy disk- the contents of the entire disk are copied: sections, information in them. This requires a second disk of the same or larger capacity.
Upgrade disk- the function is primarily needed to transfer Windows to a new larger hard drive. The partition is copied and enlarged in proportion to the size of the new hard disk.
Delete all partitions- delete all sections.
Wipe disk- the same as the previous point, only with special deletion algorithms, due to which the information will be impossible to recover.
Surface test- Checking the surface of the disk (physical). Allows you to detect bad sectors (the so-called "bad", "bad blocks").
View properties- display information about the disc.
Yes, knowledge of English is clearly required here, especially when you consider that almost every item calls up a window with settings for the action to be performed. After you make the necessary manipulations, you need to apply the changes by clicking the button Apply(Apply):
Only then will the partition change begin. This process can take some time - from a couple of minutes to several hours.
Depending on whether the system partition is affected or not, the operations are carried out either immediately in the window, or you will need to restart the computer and start changing the partition in Native mode:
The program has a lot of functions, it's hard to list them all. I recommend that you read the help for EaseUS Partition Master. It is in English, unfortunately, but you can use the Google translator. The translation is quite understandable.
Pros of EaseUS Partition Master Home Edition:
- There are a lot of functions.
- All actions are "virtual" until the Apply button is pressed. So, you can undo operations before this "point of no return" and try to do something else with the partitions. Or not at all if you change your mind.
- Works consistently and predictably. For example, during testing while changing partitions, I started copying files to the partition to be changed. Bottom line - a window appeared stating that the partition could not be locked, all operations were interrupted, the data did not disappear anywhere.
- The program is free for home use.
Cons of EaseUS Partition Master Home Edition:
- The interface is in English only.
- There are probably too many opportunities - this can confuse beginners.
- A serious failure during the operation will lead to serious consequences.
- For example, if you turn off the computer while changing the partition, the data on the partition will disappear. However, this is a minus of absolutely all programs for changing partitions.
Output: the program is good. You can and should use it, there is no alternative among free programs.
Paragon Partition Manager 11 Free
Free program for changing partitions from a company based in Russia. Unfortunately, the program is in English. What made the developers take such a step is not clear. Moreover, the paid version of the program is Russian.
The main window of the program is no different from the hero window of the previous review, except that the buttons have changed their order:
Deserves special mention Express Mode(Simplified mode). By clicking on this button, we will get a window with a list of the most frequent actions:
One could say that this is an ideal mode for beginners, if not for one "but": everything here is in English. Moreover, I had a suspicion that the English here was somehow wrong, as if it was not a person who translated, but a machine.
Pros of Paragon Partition Manager 11 Free:
- Many windows are clear enough to understand the functions.
- Some operations are carried out directly in the program window, some (if required) in Native mode. That is, the program does everything to reduce the chance of data loss.
- The program is free to use at home.
Cons of Paragon Partition Manager 11 Free:
- English-speaking, and because of the strange construction of phrases, it is quite difficult to perceive.
- The simplified Express Mode works exactly the opposite: first, the descriptions of operations and the operations themselves have more technical subtleties than required; secondly, this mode is very capricious and does not really work, giving out meaningless errors.
- The program is running too slowly. For example, it took me about 5 minutes to delete a 38GB hard drive partition - long enough for such a simple operation.
Output: the program works, but somehow unpredictable. I do not recommend using this program, since there is an alternative in the form of EaseUS Partition Master Home.
Changing partitions during installation of Windows 7, 8, 10
This tool deserves a mention too.
We take any installation disk with Windows Vista, Windows 7, 8 or 10, start the installation of the disk, go to the partition selection and click Disk setup:
Everything seems to be simple: you need to click on a section in the list, then the action button. Unfortunately, there is little action here: deletion, formatting, partition creation and expansion.
You can, for example, delete a partition and, at the expense of the free space, increase the size of another partition or partitions (selecting the desired partitions, press the Delete and Expand buttons one by one).
Alas, a very popular operation - reducing the size of partitions - is not here. You can delete a partition, then re-create a new one with a smaller partition, but, unfortunately, we will lose data in this case.
All operations take place in real time, i.e. after pressing the button, the action takes place.
Outcome: editing partitions during Windows setup is a very primitive tool. Works, but performs only a limited list of actions, among which the only one that saves data is increasing (expanding) the size of the partition. If you need to install Windows and do not need to save data on partitions, then the tool will come in handy.
If suddenly you accidentally deleted a partition during Windows installation or through any program, do not despair - the partition recovery function is available in EaseUS Partition Master Home Edition.
In order to recover a deleted hard disk partition, do not touch sections, immediately boot into Windows (or insert the hard drive into another computer if you deleted the system partition and Windows cannot boot), then run the above program, click on the line with the word in the list Unallocated("Unassigned"), then click Partition recovery.
The rest, as they say, is a matter of technology - the action wizard will tell you where to click, where to tick, then restore your deleted disk.
Tip # 2: Install two or more Windows operating systems on one hard drive
All it takes is several sections. If the hard disk already has a second partition, which is visible in the window " A computer"- make sure that there is at least 20 GB of free space (more is better), then during Windows installation, simply specify this second (third, fourth, etc.) drive. Once installed, you will be able to select Windows using the menu that appears when you turn on your computer.
If you have one disk ( C), I suggest the simplest option: Through Disk management first give the section WITH command Shrink, having reduced by at least 20 gigabytes (or better - more, because in addition to Windows, you will also install programs):
Right-click on the C drive ...
After pressing the button Shrink disk size C decreases, unallocated (free) space appears in the partition map:

We indicate unallocated space. The section will be created by the installer itself.
After installation, you will have two operating systems. You can make more unallocated spaces or empty disks, specify them for installation.
Thanks to reader Vladimir for bringing up this topic.
You may have noticed that in the screenshots of the Disk Management window, all partitions are marked with a blue stripe. You may have sections with green stripes. What is the difference between the blue and green sections?
A green bar in Disk Management is a sign of an extended (additional) partition. As I already wrote above, inside there may be "nested" sections, which from the user's point of view are no different from the main (primary) sections. Nested partitions have one peculiarity - if you reduce their size, then due to the free space that appears, it will not be possible to expand the main partition just like that. You must first compress the extended partition itself (which stores free space and a smaller partition) in order to create free space outside any partitions, only then you can expand the disks.
Standard Disk Management does not know how to work normally with extended disks, so if you see green marks instead of blue ones, it is better to use the free programs above - they will reduce extended partitions, move free space where necessary and expand the main disk.
We talked about how to create an AOMEI PE Builder Live CD. In this article, I decided to tell you how to partition a hard drive using Windows and the free AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard Edition.
Why share a hard drive at all? Many laptops and computers are sold with an unbroken hard drive. exists on disk only one sectionC: for system and data and additional service sections for programs from laptop manufacturers.
There is a saying, “Don't keep all your eggs in one basket.” The same is the case with your hard drive in the computer, where your operating system (Windows XP, 7, 8, 10) and your data (documents, photos, music, movies and other data) stored on one section Your disk. This is not good, because if an error occurs on the C: partition (drive C :), all data on this partition, including your data, is jeopardized. Secondly, when reinstalling Windows, if you have only one partition, you need to rewrite all your data from this partition to another location, which takes a lot of time with a large volume and there is not always an external hard drive or a large flash drive where this data can be overwritten. And thirdly, it is always convenient to have two or more partitions (disks) to share systems and data. In this article I will tell you and show you how to divide your hard drive into two partitions (drive C and drive D). There is no particular difficulty in this, but you need to be careful, as there is a risk of losing data, but the risk of losing is always in our life but if you read this article to the end, then everything will become clear even to a child. But it will be better if you create a backup of the data in advance, as I described how to do it. So let's get started ...
How to partition a hard drive by meansWindows
Friends, to partition the hard drive using Windows, you need to go to " Computer management". In Windows 8, for this we right-click in the lower left corner of the screen and select " Disk management»
In Windows 7, go to the menu " Start" and right-click on " A computer"And in the context menu select" Control", Then select" Disk management»


The window “ Disk management". We see that the hard drive of our computer (laptop) is divided into partitions. In this case, into two partitions: reserved by the system (350 MB), it contains the Windows boot files and the system partition C: (24 GB), on which the Windows system is installed.
You may have a disk divided into three or even four partitions (depending on the laptop model), but this does not change the essence of this, since these partitions are most likely inaccessible to you and are used for utilities of laptop manufacturers.
We are interested in section C: (marked in red in the photo), and we must divide it (split) into two parts (section C: and section D :)
Do not be surprised that in the photo I have a small hard drive (25 GB), since I am showing the whole process in a virtual machine where a hard drive of this size is installed, all actions will take place on a physical computer or laptop. But this does not change the process of partitioning the hard drive. All pictures are clickable.

Right-click on section C: and select “ Shrink Volume ...»

The system polls the hard disk volume to determine where to compress

In the next window indicate the size of compressed space in MB, that is, we indicate how much we will compress the partition, so that then this space can be given for a new disk partition and press the button " Shrink". We mean that the size of the compressed space is indicated in MB (megabytes), so if you want, for example, to create a new partition with a size of 250 GB (gigabytes), then multiply this figure by 1024 (in 1 GB - 1024 MB), we get 250 * 1024 = 256000 MB.
We also take into account that the system may not give us so much space, since it is already occupied by data.
And one more thing: the standard Windows disk management tools can be “stubborn” and do not give as much space as you “ask for”, although you have free space. This can be caused by a number of reasons, one of which is data fragmentation on this partition. In this case, you need to use special disk management programs, one of which I describe Further in this article. We read, we are not distracted 🙂

After compressing the partition, we see that now we have a C: partition, and there is additional unallocated space ...

Now we need to create a section from this unallocated space, for this we right-click on it and select “ Create Simple Volume ...»

The wizard for creating simple volumes appears, in which we click " Further»

We indicate the size of our volume in MB and click " Further»
Note:

We assign a letter to our new partition (disk). Click " Further»

We format our new section with the option “ Quick format", Click" Further»

We see that the wizard has completed the creation of the volume (partition) with the parameters that we specified at the beginning .. Press the button " Ready»

We see our two partitions in the disk management window: a reduced partition C: and a new partition E:

Voila! We go to " My computer"And we see our created additional disk

This is how you can partition a hard drive using Windows tools, but this method does not always work or does not always work as expected, so we will consider another option for managing hard drives, this is the multifunctional and free program AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard Edition. With the help of it we will do the same and additionally I will show its other main functions.
How to partition a hard drive with a free program
To install the program AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard Edition, go to the official website of the program: and click " DownloadFreeware»

We press the button " Download now»

The program will start downloading to your computer. After downloading, run this file to install

Installation of the program is simple, see screenshots (pictures are clickable) ...
To scroll through the pictures, press “ Back" or " Forward»



After installation, run the program AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard Edition
The main window of the program

We see that the C: partition (drive C :) is large and you can “unfasten” the second partition from it. Usually a 60-150 GB partition is sufficient for the C: drive, I usually leave 80 GB.
Now what are we going to do. We will compress the C: drive (change the partition), and use the freed space for a new partition (drive D :). What do we need for this? This program is both bubble and mindfulness.
So, right-click on the C: section and select “ Resize Partition»

Enter a new size for the partition. To do this, use the left mouse button to “grab” the right circle of the section and move it to the left. ... Or specify the size of the section in numbers in the field “ Partition size»

Something like the photo below. I resized the C: partition to 80GB. Click " OK»

Now, in the main window of the program, we see that our disk has unallocated space for a new partition (s). Let's take advantage of this 🙂 and create a new partition in this disk space. To do this, right-click on the unallocated space and select “ Creating a section»

We indicate the size of our new partition, the program by default offers all free space, select the drive letter and click " OK»
Note: If you want to create more than one section, then indicate the desired section less than the recommended maximum, and use the rest of the space for another section.

To apply all these actions, you need to click the " Apply»

The window " Deferred operations", Where the program shows what operations it will do with our hard disk before reaching the final result. If you agree with the actions of the program, click " Go to»

The program requires a restart, we agree and click " Yes»

After rebooting, the program waits for 10 seconds. We do not press anything during this time. If you want to cancel, press any key ...


We make sure again, go to " My computer"And rejoice!

Well, that you liked the free version of the program AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard Edition?. I like it. In addition to the fact that the program can divide disks, I will list a number of its main functions:
- Migration of the operating system to SSD / HDD disks;
- Increase, change, move, merge sections;
- Copying a disk / partition;
- Creating, deleting, formatting sections;
- Creating a bootable CD-ROM;
- MBR recovery;
- Conversion from MBR to GPT disk and vice versa without data loss;
- Recovering partitions;
- Testing the surface of the disc;
- Aligning partitions and speeding up drives, especially SSD drives;
- Converting FAT / FAT32 File System to NTFS
The program supports all types of drives: HDD / SSD hard drives with MBR / GPT disk partition styles, RAID arrays, flash drives.
Here is my video on how to partition a hard drive with the free AOMEI Partition Assistant Standard Edition
Contest "Like - Get the Key"!

Friends, there paid version programs, . In the paid version of the program, in addition to the standard functions described above, additional functions are available:
- Converting a section from main to logical and vice versa;
- Allocation of free space from a partition to another partition;
- Creation and work with dynamic disk partitions;
- Converting a dynamic disk to a basic disk;
- Changing the type of section;
- Changing the serial number of the hard drive;
- Free technical support
Full list on the page:
It just so happens that I have 3 license keys for the program AOMEI Partition Assistant Pro Edition cost 32 $ (about 1800 R. for May 2015) and I want to arrange for you contest and play these keys among your readers!
Competition conditions are simple:
- You need to click a little lower on one of the social media buttons
- In the comments, provide a link to your social network profile.
Summarizing:
June 6, 2015 i will play these 3 Keys among those who clicked on one of the social buttons. networks (shared information about the draw) and showed this profile in the comments.
I will assign a serial number to each participant. The selection of the winners will be randomly determined using a random number generator on the service www.randstuff.ru/number/ .
No more than one is accepted from each participant “ Laika”In one social network. There will be three winners... Each will get one license key.
The winners of the competition will receive license keys for the program AOMEI Partition Assistant Pro Edition and will be able to fully use all the functions of this wonderful program. Well, have we started? Who is first? 🙂