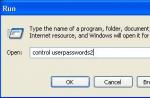
A situation often arises when the question becomes relevant: “How to connect two phones to each other?” For example, you need to copy a large file with a video or program from one phone to another. Or move a large number of music records and photos. In addition to the traditional sending of files via Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, there are several other methods. This article will tell you how to connect two smartphones with a USB cable.
Is it possible to connect smartphones with a cable?
In order to connect two phones with a cable, you need to have a micro-USB - USB cable and a USB-female adapter for OTG. To begin with, it is worth noting that only those phones that support the One-touch-Go (OTG) function can be connected. Thanks to this technology, you can connect any peripheral device, including the second phone.
USB adapters can be marked “master” or “slave”, that is, they can be master and slave. If there is an adapter marked “master”, then the phone with this adapter will be the main one, and the second phone will be displayed on its screen as removable media. If the adapter is marked “slave”, then the situation will be mirrored.
All modern smartphones support OTG technology. It was designed to connect keyboards, webcams, removable media, printers, mice, and other peripherals to Android devices.
To connect two phones, you first need to connect a USB-female adapter to one phone, and a micro-USB cable to the second phone. Once your phones have identified the cable and adapter, you can safely connect them to each other.
When connecting two phones, you do not need to use an additional software. To do this, the interface of a standard smartphone file manager is sufficient. In this case, the contents of the slave phone are displayed in file manager main phone as the contents of removable storage. After connecting the phones with a cable, you can copy files at high speed and not worry about a possible connection break or data loss, as is the case with data transfer via Bluetooth.
How to connect a smartphone to a tablet?
Tablets are no less popular than smartphones today. And therefore the question of how to connect a tablet to a phone with a USB cable arises quite often. Moreover, most modern users often have both of these devices. And sometimes you really need to quickly copy a large amount of information from one of them to another.
As in the situation with two phones, a micro-USB to USB cable and a USB-female adapter for the OTG function will come to our aid. But some tablets already have a built-in USB interface. In this situation, the task is simplified: all you need to connect is a micro-USB to USB cable. Just remember that the built-in USB-female often has a “master” manufacturer’s mark, and take this into account when connecting.
Once you know how to connect your phone and tablet via a USB cable, transferring information between these two devices has become even faster and more reliable. Of course, in the world of wireless technology, this capability is not always necessary. But situations happen different. For example, on one of the devices it is broken Wi-Fi adapter. Then transferring data via a USB interface will be the only and no less reliable way.
Telephone is an electrical device that allows people to exchange information over a distance using an electrical signal. The word telephone came to us from ancient Greece. Tele is translated as “far”, and background is “voice”.
After reading the article, any home craftsman can easily connect a landline, fax, or several parallel telephones, including a radiotelephone.
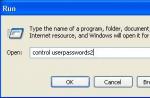
What is the voltage in the telephone line
The telephone communication line is under a DC voltage of 40-60 V if the telephone is not connected or is connected, but the handset is placed on the telephone set. During a call, the voltage in the communication line becomes variable with an amplitude of up to 120 V. When you pick up the phone, the voltage drops to 6-12 V. This voltage is not life-threatening, but it can cause discomfort.
It is impossible to damage the communication line or damage the telephone when connected. Shutdown may occur telephone line for a few minutes if the handset is picked up for a long time without dialing a number or if the communication line conductors are short-circuited. The telephone line is automatically switched off by an automatic telephone exchange (PBX) to save energy. So you can safely start connecting your phone to the communication line yourself.
Before connecting a landline telephone, fax or radiotelephone to the communication line, it is advisable, but not necessary, to check that the communication line is ready. The line voltage can be measured with a voltmeter designed to measure DC voltage.
If the phone is not connected to the line or is connected, and the handset is on the phone, the device should show a voltage of 40-60 V. If there is no voltmeter, you can check using a potato, and this is not a joke, but real way checks. It is enough to stick the noodle wires, stripped of insulation, into the cut of the potato. No batteries are needed since the wires are already energized.
What current will flow
in case of short circuit of telephone line wires
The PBX has a system installed to protect against failure of equipment and communication lines, which limits the current when short circuit telephone line up to 40 mA.
For the communication line, one of the free pairs, brown or blue, is taken. A twisted pair consists of two conductors twisted together. The insulation of one of them is painted a solid color, and the insulation of the second is white with stripes of the color of the first.
Having two telephone sets, a coil of two-core wire of sufficient length and a small number of radio components, you can organize your own telephone line for two subscribers. For example, arrange a connection between two neighboring apartments by throwing a wire between the windows, or between neighboring country houses, between a house and a gazebo. First of all, let’s remember from our school physics course how a telephone works. In the simplest case, these are two telephone capsules connected to each other by a two-wire line.
When one speaks in front of one capsule, its magnetic membrane moves from sound waves and induces some alternating voltage in the coil, which is supplied through wires to the coil of the second capsule and sets its membrane in motion. It turns out that the membrane of the second capsule moves in the same way as the first, creating sound waves that can be heard. But theoretically, such a connection is ineffective, the losses in the wires are too large and the efficiency of the capsule is low.
Therefore, a real telephone set has a carbon microphone, the resistance of which changes in time with speech. In addition, some constant voltage is supplied to the line. The result is that a carbon microphone connected to the line, changing its resistance in time with speech, causes a change in the current strength in the line.
Thus, an alternating current is obtained in the line, which changes in time with speech. This current powers the capsule of another telephone and emits sound waves that are quite distinct and loud.
A schematic diagram of a simple telephone line is shown in the figure. Two electronic telephone devices are used - handsets with push-button dialers, but you can also take simple ones
disk devices. They are connected to each other by two wires. These wires are supplied with a constant voltage of 60-80V through resistance R1. When the tubes of both TAs are hung between these wires, there is a voltage of 60-80V, since in this state the internal resistances of the TAs are very high.
Suppose we pick up the handset TA2, while its lever switch connects its conversation node to the line and the resistance of TA2 decreases sharply, so much that the voltage in the line drops to 8-10V (the voltage drops because from the resistor R1 and the resistance of the conversation node TA is obtained voltage divider, and the line turns out to be connected precisely through this divider).
If you start speaking in front of the TA2 microphone, the resistance of its conversation unit begins to change in time with the speech, which means the overall resistance of TA2 also changes. In this case, R1 remains unchanged and the voltage in the line changes in time with speech. The TA1 telephone is also connected to this line, and if you pick up its handset, you can hear what is being said in front of the TA2 microphone. If subscriber TA1 answers, subscriber TA2 will hear his voice. This way you can talk to each other.
To call a subscriber, the telephone set has a bell or buzzer; it is connected to the line whenever the handset is hung up and reacts to any significant voltage drop in the line. If you pick up TA2, the TA1 bell will “ring” once, because there was one voltage drop in the line, hang up and TA1 will “ring” again.
The telephone station contains a dialer, push-button or rotary, it doesn’t matter, in any case it serves to create voltage drops in the line; the telephone exchange receives these drops, counts them and thus determines the subscriber’s number. In our case, there is no telephone exchange, but the dialer can be used to call a subscriber. If you dial the number “9”, the TA creates nine voltage drops in the line, which means that the second TA “rings” not once but nine times, if the number “0” - ten times.
Thus, in order for you to call your friend on TA1 from the TA2 phone, you need to pick up the TA2 handset and dial “O” (or another number) several times in a row. As a result, TA1 will ring, your friend will hear the call, and by picking up the phone he will be able to talk to you. In the same way, you can call TA2 from the TA1 device.
The DC voltage for powering the line is obtained from mains voltage 220V using transformer T1 and rectifier with diodes VD1-VD4. Rectified voltage ripples are smoothed out by capacitor C1. Transformer T1 can be made from a small-sized transformer from a network source to power toys or portable equipment. It is necessary to disassemble the source housing and connect the transformer using an extension cord to the network and measure the voltage on its secondary winding. Let's assume the voltmeter shows 6V.
We need 50 V. Now we disconnect the transformer from the network, disassemble its plate core and unwind the secondary winding (not the mains winding), carefully counting its turns. Let's say we counted 120 turns, this despite the fact that the output voltage was 6V. Now we calculate how many turns this transformer has per 1V: 120 / 6 = 20, a total of 20 turns. We need 50 V, which means the secondary winding must contain 20x50 = 1000 turns. We take a thin winding wire, for example PEV 0.06 or PEV 0.09, and carefully wind 1000 turns with this wire instead of the old secondary winding.
Then we assemble the transformer core. You can take a ready-made transformer that produces at least 36V and at most 50V.
D226 diodes can be replaced with any rectifier, for example D7 or modern KD102, KD103, KD105, KD226, KD209. Capacitor C1 for a voltage of at least 100V and a capacity of at least 160 µF. Resistor R1 with a resistance of 1 kOhm to 1.8 kOhm for a power of at least 2 W. Toggle switch S1 of any type.
Structurally, the power supply can be connected to the line anywhere, near TA2, near TA1, or even in the middle. For example, if TA2 is in an electrified room, and TA1 is in a garden gazebo, it is clear that the source is connected near TA2.
When installing, do not mix up the polarity of connecting capacitor C1 and diodes. D226 diodes have a graphic image of the diode on the body, along the body, so that you can understand the purpose of the terminals.
Hello, dear lovers of experiments and DIY experiments!
We have already touched on the topic of telephone communication on the pages of the DIY science and technology blog. Back then we were talking about a phone made from plastic cups. Unfortunately, such a telephone demonstrates very well some of the laws of acoustics, but in practice it can only be used in fairly ideal conditions - the telephone thread must be taut and must not touch any obstacles. Yes, and the length of the thread is limited. Ordinary is another matter landline phone. There is no doubt about its applicability. Despite the spread mobile communications, it will not soon be forced out of apartments and offices. We’ll talk about it, and at the same time we’ll build our own simple telephone network, devoid of the above-mentioned disadvantages.
Did you know that telephone communication officially dates back to the 19th century, and since then the basic design of the telephone has remained virtually unchanged? This is true. Of course, the phone has changed in detail - a modern telephone includes electronic components that simply did not exist at the time of its invention. In telephone networks there are automatic telephone exchanges that switch subscribers among themselves. Various telephone services have appeared. However, the purpose of a telephone set of any circuit has remained unchanged since its invention by Alexander Bell in 1876 - converting sound into an electrical signal and transmitting it along a communication line to the desired subscriber and converting it back into an audio signal. And in this classic telephone connection there is no equal.
To demonstrate this point, let's compare the above-mentioned plastic cup phone to a regular telephone network. We have already talked about the disadvantages of the first - it is a short range, the absence of obstacles in the path of the communication line, and ensuring thread tension. In addition, let's estimate the speed of sound propagation in the first and second types of communication. Thus, the speed of propagation of a sound wave in iron is approximately 5000 meters per second. Even if we found a way to eliminate sound wave attenuation, sound from, say, Moscow to Vladivostok would take 30 minutes! I don’t know about you, but I would quickly get tired of such a phone - the radio signal reaches Mars faster! Another thing is the speed of propagation of an electrical impulse - 300,000 kilometers per second. There is no better intermediary for sound transmission. You just need to come up with a way to convert a sound wave into an electrical signal and vice versa. And this is exactly the method that Alexander Graham Bell found.
In his telephone set, the sound signal was converted into electrical impulses, which reached the opposite device through wires and were converted there back into a sound signal. Everything turned out to be as simple as it was ingenious! Of course, in the first telephone network there were no telephone exchanges, no dialers, or other modern telephone delights. There were only two telephone sets connected to each other by an electric wire. I suggest you check the possibility of the existence of such a telephone network. Moreover, such telephone communication It is quite possible to use it in practice, for example, to install telephones in a home workshop. And if you take such a phone to your child’s place of play, it will remain a key link in many games for a long time.
So, we will need:
- two telephone sets;
- electrical wire.
- DC source.
- telephone patch cord.

As for the electrical wire - there is no need to limit yourself - any length of telephone wire can be used for your experimental or home needs. The type of wire can also be almost any. In my experiments I used 30 meters of twisted pair cable.
As for the DC source, we can say the following. In the telephone network, the voltage on the line at rest (when the phone is on-hook) is 60 volts. But for our experiments, the voltage from two Krona batteries will be sufficient. You can also use a 12-20 volt power supply.
Take the patch cord and cut it in half.

We clean the ends. The strands of the patch cord are often very thin, and it can be inconvenient to simply strip them with a knife. You can burn them.


If you use batteries, connect them in series. It is convenient to use clip-on contacts, but you can do without them.

We connect our current source to the circuit in series, that is, to the break of one of the wires.


Don't forget to insulate the contacts.
That's it, you can use it! The only significant drawback of this scheme is the inability to call a subscriber. To ensure this possibility, it is necessary either to supply alternating voltage to the line, as is done in city networks, or to install an additional line to provide sound or light calls.